ATBF1 inhibits estrogen receptor (ER) function by selectively competing with AIB1 for binding to the ER in ER-positive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20720010
- PMCID: PMC2963406
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128330
ATBF1 inhibits estrogen receptor (ER) function by selectively competing with AIB1 for binding to the ER in ER-positive breast cancer cells
Abstract
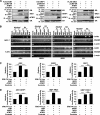
Loss of the q22 band of chromosome 16 is a frequent genetic event in breast cancer, and the candidate tumor suppressor gene, ATBF1, has been implicated in breast cancer by genomic deletion, transcriptional down-regulation, and association with better prognostic parameters. In addition, estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer expresses a higher level of ATBF1, suggesting a role of ATBF1 in ER-positive breast cancer. In this study, we examined whether and how ATBF1 affects the ER function in breast cancer cells. We found that ATBF1 inhibited ER-mediated gene transcription, cell growth, and proliferation in ER-positive breast cancer cells. In vitro and in vivo immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that ATBF1 interacted physically with the ER and that multiple domains in both ATBF1 and ER proteins mediated the interaction. Furthermore, we demonstrated that ATBF1 inhibited ER function by selectively competing with the steroid receptor coactivator AIB1 but not GRIP1 or SRC1 for binding to the ER. These findings not only support the concept that ATBF1 plays a tumor-suppressive role in breast cancer, they also provide a mechanism for how ATBF1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer.
Figures
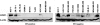
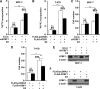
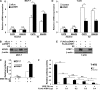
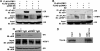

Similar articles
-
Estrogen up-regulates ATBF1 transcription but causes its protein degradation in estrogen receptor-alpha-positive breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 22;286(16):13879-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187849. Epub 2011 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21367855 Free PMC article.
-
Atbf1 regulates pubertal mammary gland development likely by inhibiting the pro-proliferative function of estrogen-ER signaling.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051283. Epub 2012 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251482 Free PMC article.
-
AIB1:ERα transcriptional activity is selectively enhanced in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 15;18(12):3305-15. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3300. Epub 2012 May 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22550166
-
p33ING1b and estrogen receptor (ER) alpha.Breast Cancer. 2004;11(1):33-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02967999. Breast Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14718790 Review.
-
Molecular action of the estrogen receptor and hormone dependency in breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2003;10(2):89-96. doi: 10.1007/BF02967632. Breast Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12736560 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of methylation changes associated with positive and negative growth deviance in Gambian infants using a targeted methyl sequencing approach of genomic DNA.FASEB Bioadv. 2021 Feb 5;3(4):205-230. doi: 10.1096/fba.2020-00101. eCollection 2021 Apr. FASEB Bioadv. 2021. PMID: 33842847 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor ZFHX3 is crucial for the angiogenic function of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in liver cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 15;295(20):7060-7074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012131. Epub 2020 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32277050 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of CTCF and ZFHX3 Mutation and Associated Outcomes in Endometrial Cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Sep 1;107(11):djv249. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv249. Print 2015 Nov. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 26330387 Free PMC article.
-
Oestrogen causes ATBF1 protein degradation through the oestrogen-responsive E3 ubiquitin ligase EFP.Biochem J. 2012 Jun 15;444(3):581-90. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111890. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22452784 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating genomic, transcriptomic and clinical data: a prognostic and stem cell-like MYC and PRC imbalance in high-risk neuroblastoma.BMC Syst Biol. 2017 Oct 3;11(Suppl 5):92. doi: 10.1186/s12918-017-0466-5. BMC Syst Biol. 2017. PMID: 28984200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Platet N., Cathiard A. M., Gleizes M., Garcia M. (2004) Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 51, 55–67 - PubMed
-
- Bryant J., Fisher B., Dignam J. (2001) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 30, 56–61 - PubMed
-
- Fisher B., Jeong J. H., Dignam J., Anderson S., Mamounas E., Wickerham D. L., Wolmark N. (2001) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 30, 62–66 - PubMed
-
- Henderson I. C. (1993) Cancer 71, Suppl. 6, 2127–2140 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

