A 24-residue peptide (p5), derived from p35, the Cdk5 neuronal activator, specifically inhibits Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and tau hyperphosphorylation
- PMID: 20720012
- PMCID: PMC2962518
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134643
A 24-residue peptide (p5), derived from p35, the Cdk5 neuronal activator, specifically inhibits Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and tau hyperphosphorylation
Abstract
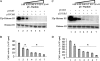
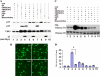
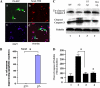
The activity of Cdk5-p35 is tightly regulated in the developing and mature nervous system. Stress-induced cleavage of the activator p35 to p25 and a p10 N-terminal domain induces deregulated Cdk5 hyperactivity and perikaryal aggregations of hyperphosphorylated Tau and neurofilaments, pathogenic hallmarks in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, respectively. Previously, we identified a 125-residue truncated fragment of p35 called CIP that effectively and specifically inhibited Cdk5-p25 activity and Tau hyperphosphorylation induced by Aβ peptides in vitro, in HEK293 cells, and in neuronal cells. Although these results offer a possible therapeutic approach to those neurodegenerative diseases assumed to derive from Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and/or Aβ induced pathology, CIP is too large for successful therapeutic regimens. To identify a smaller, more effective peptide, in this study we prepared a 24-residue peptide, p5, spanning CIP residues Lys(245)-Ala(277). p5 more effectively inhibited Cdk5-p25 activity than did CIP in vitro. In neuron cells, p5 inhibited deregulated Cdk5-p25 activity but had no effect on the activity of endogenous Cdk5-p35 or on any related endogenous cyclin-dependent kinases in HEK293 cells. Specificity of p5 inhibition in cortical neurons may depend on the p10 domain in p35, which is absent in p25. Furthermore, we have demonstrated that p5 reduced Aβ(1-42)-induced Tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in cortical neurons. These results suggest that p5 peptide may be a unique and useful candidate for therapeutic studies of certain neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures



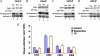


Similar articles
-
A peptide derived from cyclin-dependent kinase activator (p35) specifically inhibits Cdk5 activity and phosphorylation of tau protein in transfected cells.Eur J Biochem. 2002 Sep;269(18):4427-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03133.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12230554
-
AAV9-Mediated Cdk5 Inhibitory Peptide Reduces Hyperphosphorylated Tau and Inflammation and Ameliorates Behavioral Changes Caused by Overexpression of p25 in the Brain.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;70(2):573-585. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190099. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31256130
-
p10, the N-terminal domain of p35, protects against CDK5/p25-induced neurotoxicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 4;109(49):20041-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212914109. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23151508 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides derived from Cdk5 activator p35, specifically inhibit deregulated activity of Cdk5.Biotechnol J. 2007 Aug;2(8):978-87. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700057. Biotechnol J. 2007. PMID: 17526058 Review.
-
Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5: role in nervous system function and its specific inhibition by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.020. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023357 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific inhibition of p25/Cdk5 activity by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces neurodegeneration in vivo.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 2;33(1):334-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3593-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23283346 Free PMC article.
-
Three decades of Cdk5.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Nov 23;28(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00774-y. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 34814918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p5 Peptide-Loaded Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Neurological Recovery After Focal Cerebral Ischemia in a Rat Model.Transl Stroke Res. 2021 Feb;12(1):125-135. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00805-0. Epub 2020 May 6. Transl Stroke Res. 2021. PMID: 32378028 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and Neuroprotective Peptide Therapies: A Case for Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs).Brain Sci. 2018 Aug 7;8(8):147. doi: 10.3390/brainsci8080147. Brain Sci. 2018. PMID: 30087289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long- and short-term CDK5 knockdown prevents spatial memory dysfunction and tau pathology of triple transgenic Alzheimer's mice.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Sep 10;6:243. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00243. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25309427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chae T., Kwon Y. T., Bronson R., Dikkes P., Li E., Tsai L. H. (1997) Neuron 18, 29–42 - PubMed
-
- Cheung Z. H., Fu A. K., Ip N. Y. (2006) Neuron 50, 13–18 - PubMed
-
- Dhavan R., Tsai L. H. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 749–759 - PubMed
-
- Lai K. O., Ip N. Y. (2009) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1792, 741–745 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

