Calibration of the TonoLab tonometer in mice with spontaneous or experimental glaucoma
- PMID: 20720229
- PMCID: PMC3053110
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-5556
Calibration of the TonoLab tonometer in mice with spontaneous or experimental glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To measure the accuracy of TonoLab (TioLat, Helsinki, Finland) tonometry in mice with spontaneous or induced experimental glaucoma.
Methods: Chronic intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation was induced in one eye of 32 mice by injection of polystyrene beads and viscoelastic material. Three to 6 weeks later, the eyes were cannulated and manometrically set to 10, 20, 30, 40, or 50 mm Hg. The mice were 8-week and 8-month-old C57BL/6, 8-week-old DBA/2J, and 8-week-old CD1. The TonoLab calibration was also tested on five aged DBA/2J mice with spontaneous glaucoma. The relation of the TonoLab reading to manometric IOP was evaluated in multivariate linear regression models with axial length, IOP history, and mouse strain as independent variables.
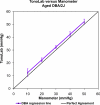
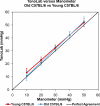
Results: The slope of the relationship between TonoLab and manometric IOP in all the mice was 0.998, with an intercept of 2.3 mm Hg (adjusted R in univariate regression = 0.86). Neither the mice with bead-induced glaucoma nor those with spontaneous glaucoma (older DBA/2J mice) differed significantly from the control animals in having an excellent correlation between TonoLab and manometer IOP. Longer and wider mouse eyes had slightly higher tonometrically measured IOP, whether glaucomatous or control (multivariate regression, adjusted R(2) = 0.90, P < 0.0001). There was no difference in tonometric accuracy among the three mouse strains: CD1, C57BL/6, and DBA/2J, nor between 8-week and 8-month-old C57BL/6 mice (multivariate regression, P = 0.32).
Conclusions: The TonoLab accurately reflects IOP in both normal mice and in eyes of mice with experimental or spontaneous glaucoma, with no detectable effect of age.
Figures




References
-
- John SW, Hagaman JR, MacTaggart TE, Peng L, Smithes O. Intraocular pressure in inbred mouse strains. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:249–253 - PubMed
-
- Avila MY, Carre DA, Stone RA, Civan MM. Reliable measurement of mouse intraocular pressure by a servo-null micropipette system. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:1841–1846 - PubMed
-
- Cohan BE, Bohr DF. Measurement of intraocular pressure in awake mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:2560–2562 - PubMed
-
- Danias J, Kontiola AI, Filippopoulos T, Mittag T. Method for the noninvasive measurement of intraocular pressure in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:1138–1141 - PubMed
-
- Grozdanic SD, Betts DM, Sakaguchi DS, et al. Laser-induced mouse model of chronic ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:4337–4346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

