DNA methylation regulates cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice
- PMID: 20720536
- PMCID: PMC3055323
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2010.128
DNA methylation regulates cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice
Abstract
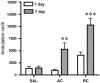
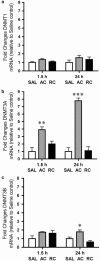
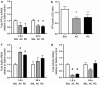
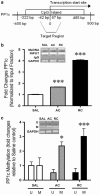
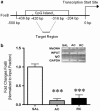
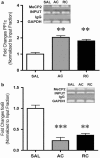
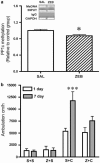
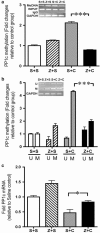
The behavioral sensitization produced by repeated cocaine treatment represents the neural adaptations underlying some of the features of addiction in humans. Cocaine administrations induce neural adaptations through regulation of gene expression. Several studies suggest that epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation, are the critical regulators of gene expression in the adult central nervous system. DNA methylation is catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and consequent promoter region hypermethylation is associated with transcriptional silencing. In this study a potential role for DNA methylation in a cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization model in mice was explored. We report that acute cocaine treatment caused an upregulation of DNMT3A and DNMT3B gene expression in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, DNA bisulfite modification, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we observed that cocaine treatment resulted in DNA hypermethylation and increased binding of methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) at the protein phosphatase-1 catalytic subunit (PP1c) promoter. These changes are associated with transcriptional downregulation of PP1c in NAc. In contrast, acute and repeated cocaine administrations induced hypomethylation and decreased binding of MeCP2 at the fosB promoter, and these are associated with transcriptional upregulation of fosB in NAc. We also found that pharmacological inhibition of DNMT by zebularine treatment decreased cocaine-induced DNA hypermethylation at the PP1c promoter and attenuated PP1c mRNA downregulation in NAc. Finally, zebularine and cocaine co-treatment delayed the development of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization. Together, these results suggest that dynamic changes of DNA methylation may be an important gene regulation mechanism underlying cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization.
Figures
References
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Berke JD, Hyman SE. Addiction, dopamine, and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron. 2000;25:515–532. - PubMed
-
- Bestor TH. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2395–2402. - PubMed
-
- Bird A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002;16:6–21. - PubMed
-
- Brami-Cherrier K, Roze E, Girault JA, Betuing S, Caboche J. Role of the ERK/MSK1 signalling pathway in chromatin remodelling and brain responses to drugs of abuse. J Neurochem. 2009;108:1323–1335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

