Vaccine Efficacy of Bm86 Ortholog of H. a. anatolicum, rHaa86 Expressed in Prokaryotic Expression System
- PMID: 20721331
- PMCID: PMC2911586
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/165812
Vaccine Efficacy of Bm86 Ortholog of H. a. anatolicum, rHaa86 Expressed in Prokaryotic Expression System
Abstract
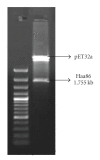
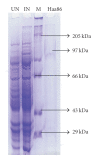
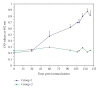
The use of tick vaccine in controlling ticks and tick borne diseases has been proved effective in integrated tick management format. For the control of H. a. anatolicum, Bm86 ortholog of H. a. anatolicum was cloned and expressed as fusion protein in E. coli as E. coli-pETHaa86. The molecular weight of the rHaa86 was 97 kDa with a 19 kDa fusion tag of thioredoxin protein. The expressed protein was characterized immunologically and vaccine efficacy was evaluated. After 120 hours of challenge, only 26% tick could successfully fed on immunized animals. Besides significant reduction in feeding percentages, a significant reduction of 49.6 mg; P < .01 in the weight of fed females in comparison to the females fed on control animals was recorded. Following oviposition, a significant reduction of 68.1 mg; P < .05 in the egg masses of ticks fed on immunized animals in comparison to the ticks fed on control animals was noted. The reduction of number of females, mean weight of eggs, adult females and efficacy of immunogen were 73.8%, 31.3%, 15.8%, and 82.3%, respectively. The results indicated the possibility of development of rHaa86 based vaccine as a component of integrated control of tick species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning, expression and immunoprotective efficacy of rHaa86, the homologue of the Bm86 tick vaccine antigen, from Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum.Parasite Immunol. 2009 Mar;31(3):111-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2008.01082.x. Parasite Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19222782
-
Efficacy of rHaa86, an orthologue of Bm86, against challenge infestations of Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2010 Apr;57(1-2):96-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2010.01107.x. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2010. PMID: 20537118 Clinical Trial.
-
Vaccine potential of recombinant antigens of Theileria annulata and Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum against vector and parasite.Vet Parasitol. 2012 Sep 10;188(3-4):231-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.03.051. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Vet Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22546546
-
Exposed and concealed antigens as vaccine targets for controlling ticks and tick-borne diseases.Parasite Immunol. 2006 Apr;28(4):155-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2006.00806.x. Parasite Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16542317 Review.
-
Tick vaccines and the transmission of tick-borne pathogens.Vet Res Commun. 2007 Aug;31 Suppl 1:85-90. doi: 10.1007/s11259-007-0069-5. Vet Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17682852 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of potential plant extracts for anti-tick activity against acaricide resistant cattle ticks, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae).Exp Appl Acarol. 2015 May;66(1):159-71. doi: 10.1007/s10493-015-9890-7. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Exp Appl Acarol. 2015. PMID: 25717008
-
Conserved Amblyomma americanum tick Serpin19, an inhibitor of blood clotting factors Xa and XIa, trypsin and plasmin, has anti-haemostatic functions.Int J Parasitol. 2015 Aug;45(9-10):613-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 May 5. Int J Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 25957161 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in vitro anti-tick efficacy of commercially available products and newly developed phyto-formulations against field collected and resistant tick lines of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus.J Parasit Dis. 2016 Dec;40(4):1590-1596. doi: 10.1007/s12639-015-0736-3. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Parasit Dis. 2016. PMID: 27876990 Free PMC article.
-
Development and field evaluation of PCR assays based on minimum length Bm86 cDNA fragments required for Rhipicephalus and Hyalomma tick species delineation.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jun 29;10:1209210. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1209210. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37456966 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses against rHaa86 in cross-bred cattle.J Parasit Dis. 2015 Jun;39(2):292-7. doi: 10.1007/s12639-013-0347-9. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Parasit Dis. 2015. PMID: 26064021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh S, Azhahianambi P, de la Fuente J. Control of ticks of ruminants, with special emphasis on livestock farming systems in India: present and future possibilities for integrated control: a review. Experimental and Applied Acarology. 2006;40(1):49–66. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, Bansal GC, Gupta SC, et al. Status of tick distribution in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Parasitology Research. 2007;101(supplement 2):S207–S216. - PubMed
-
- Minjauw L, McLeod A. DFID Animal Health Programme. Edinburgh, UK: Centre for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, University of Edinburgh; 2003. Tick borne diseases and poverty. The impact of tick and tick borne diseases on the livelihoods of small-scale and marginal livestock owners in India and eastern and southern Africa.
-
- Graf J-F, Gogolewski R, Leach-Bing N, et al. Tick control: an industry point of view. Parasitology. 2004;129:S427–S442. - PubMed
-
- de la Fuente J, Kocan KM. Advances in the identification and characterization of protective antigens for recombinant vaccines against tick infestations. Expert Review of Vaccines. 2003;2(4):583–593. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
