MLCK-independent phosphorylation of MLC20 and its regulation by MAP kinase pathway in human bladder smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20722044
- PMCID: PMC5664925
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20471
MLCK-independent phosphorylation of MLC20 and its regulation by MAP kinase pathway in human bladder smooth muscle cells
Abstract
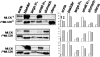
Myosins are a superfamily of actin-based molecular motor proteins, which hydrolyze ATP and generate various forms of eukaryotic motility and muscle contraction. Myosin light chain 20 (MLC20) is small ring around the neck region of heavy chain of myosins. Phosphorylation of MLC20 is thought to play a key role in regulation of smooth muscle contraction. Calcium- and calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is considered the primary regulator of MLC20 phosphorylation. However, several observations in smooth muscle contraction cannot be explained by the mode of phosphorylation. By performing a series of experiments in vitro and in vivo, we report here MLCK-independent MLC20 phosphorylation. Gene expression study reveals that expression of MLCK in smooth muscles is inconsistent with MLC20 phosphorylation at Ser19. None of inactivating calmodulin/MLCK, depriving of calcium and silencing MLCK expression by siRNA blocks effectively the phosphorylation of MLC20 at Ser19. In addition, by overexpressing active human MAP (mitogen-activated protein)-ERK kinase kinase-1 (MEKK1) and blocking its downstream messengers, we have demonstrated a new regulatory system of MLC phosphorylation via MEKK1, which downregulates Ser19 phosphorylation of MLC20 through its downstream molecules, p38, JNK, and ERK in human bladder smooth muscle cells.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
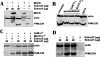


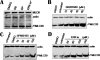



Similar articles
-
Gi-coupled receptors mediate phosphorylation of CPI-17 and MLC20 via preferential activation of the PI3K/ILK pathway.Biochem J. 2006 May 15;396(1):193-200. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051772. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16472257 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin light chain kinase activation and calcium sensitization in smooth muscle in vivo.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):C358-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.90645.2007. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18524939 Free PMC article.
-
A temporal Ca2+ desensitization of myosin light chain kinase in phasic smooth muscles induced by CaMKKβ/PP2A pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Sep 1;321(3):C549-C558. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34106787
-
Signaling for contraction and relaxation in smooth muscle of the gut.Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:345-74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.68.040504.094707. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16460276 Review.
-
Myosin light chain kinase as a multifunctional regulatory protein of smooth muscle contraction.IUBMB Life. 2001 Jun;51(6):337-44. doi: 10.1080/152165401753366087. IUBMB Life. 2001. PMID: 11758800 Review.
Cited by
-
Protease-activated receptor 2 activates CRAC-mediated Ca2+ influx to cause prostate smooth muscle contraction.FASEB Bioadv. 2019 Apr;1(4):255-264. doi: 10.1096/fba.2018-00024. Epub 2019 Jan 3. FASEB Bioadv. 2019. PMID: 31198907 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia modulates the expression of leucine zipper-positive MYPT1 and its interaction with protein kinase G and Rho kinases in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Pulm Circ. 2011 Oct-Dec;1(4):487-98. doi: 10.4103/2045-8932.93548. Pulm Circ. 2011. PMID: 22530104 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of myosin light chain kinase inhibition on contractility, force development and myosin light chain 20 phosphorylation of rat cervical and thoracic duct lymphatics.J Physiol. 2011 Nov 15;589(Pt 22):5415-29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.218446. Epub 2011 Sep 19. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21930597 Free PMC article.
-
Calponin-3 deficiency augments contractile activity, plasticity, fibrogenic response and Yap/Taz transcriptional activation in lens epithelial cells and explants.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 28;10(1):1295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58189-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31992794 Free PMC article.
-
Vasoactivity of rucaparib, a PARP-1 inhibitor, is a complex process that involves myosin light chain kinase, P2 receptors, and PARP itself.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 17;10(2):e0118187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118187. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25689628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271(34):20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Nakamura N, Fukata Y, Yano T, Shibata M, Ikebe M, Kaibuchi K. Myosin II activation promotes neurite retraction during the action of Rho and Rho-kinase. Genes Cells. 1998;3(3):177–188. - PubMed
-
- Betapudi V, Licate LS, Egelhoff TT. Distinct roles of non-muscle myosin II isoforms in the regulation of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell spreading and migration. Cancer Res. 2006;66(9):4725–4733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

