Dose-dependent effects of the once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide in patients with Type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 20722676
- PMCID: PMC3068287
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03020.x
Dose-dependent effects of the once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide in patients with Type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the dose-response relationship of lixisenatide (AVE0010), a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in metformin-treated patients with Type 2 diabetes.
Methods: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, 13 week study of 542 patients with Type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled [glycated haemoglobin (HbA(1c)) > or = 7.0 and < 9.0% (> or = 53 and < 75 mmol/mol)] on metformin (> or = 1000 mg/day) treated with subcutaneous lixisenatide doses of 5, 10, 20 or 30 microg once daily or twice daily or placebo. The primary end-point was change in HbA(1c) from baseline to 13 weeks in the intent-to-treat population.
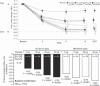
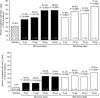
Results: Lixisenatide significantly improved mean HbA(1c) from a baseline of 7.55% (59.0 mmol/mol); respective mean reductions for 5, 10, 20 and 30 microg doses were 0.47, 0.50, 0.69 and 0.76% (5.1, 5.5, 7.5 and 8.3 mmol/mol), on once-daily and 0.65, 0.78, 0.75 and 0.87% (7.1, 8.5, 8.2 and 9.5 mmol/mol) on twice-daily administrations vs. 0.18% (2.0 mmol/mol) with placebo (all P < 0.01 vs. placebo). Target HbA(1c) < 7.0% (53 mmol/mol) at study end was achieved in 68% of patients receiving 20 and 30 microg once-daily lixisenatide vs. 32% receiving placebo (P < 0.0001). Dose-dependent improvements were observed for fasting, postprandial and average self-monitored seven-point blood glucose levels. Weight changes ranged from -2.0 to -3.9 kg with lixisenatide vs. -1.9 kg with placebo. The most frequent adverse event was mild-to-moderate nausea.
Conclusions: Lixisenatide significantly improved glycaemic control in mildly hyperglycaemic patients with Type 2 diabetes on metformin. Dose-response relationships were seen for once- and twice-daily regimens, with similar efficacy levels, with a 20 microg once-daily dose of lixisenatide demonstrating the best efficacy-to-tolerability ratio. This new, once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist shows promise in the management of Type 2 diabetes to be defined further by ongoing long-term studies.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards for diabetes care—2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:S12–S54. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Global Guideline for Type 2 Diabetes, 2005. Available at http://www.idf.org/home/index.cfm?node=1457 Last accessed 29 January 2009.
-
- Alvarez Guisasola F, Mavros P, Nocea G, Alemao E, Alexander CM, Yin D. Glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in seven European countries: findings from the Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management (RECAP-DM) study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10(Suppl 1):8–15. - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ. Enhancing incretin action for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2929–2940. - PubMed
-
- Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S. Glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

