Histamine H(4) receptor activation on human slan-dendritic cells down-regulates their pro-inflammatory capacity
- PMID: 20722760
- PMCID: PMC3015074
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03336.x
Histamine H(4) receptor activation on human slan-dendritic cells down-regulates their pro-inflammatory capacity
Abstract
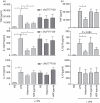
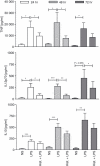
6-Sulpho LacNAc dendritic cells (slanDC) are a major population of human blood DC that are highly pro-inflammatory, as characterized by their outstanding capacity to produce tumour necrosis factor-α and interleukin-12 (IL-12) and to prime antigen-specific T-cell responses. SlanDC were found to be present in inflamed tissue such as atopic dermatitis, where high levels of histamine are also present. As histamine is an important regulator of allergic inflammation we investigated the role of histamine receptors, particularly the most recently identified histamine H(4) receptor (H(4) R), in modulating the pro-inflammatory function of slanDC. The expression of H(4) R was evaluated by real-time PCR and flow cytometry. Cytokine production in response to H(4) R stimulation was assessed by intracellular flow cytometric staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We show that slanDC express the H(1) R, H(2) R and H(4) R on mRNA and the H(4) R on protein level. No differences were observed in basal H(4) R expression in patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but in atopic dermatitis patients the H(4) R was up-regulated by interferon-γ. When stimulated with lipopolysaccharide in the presence of histamine, slanDC produced substantially lower levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor-α and IL-12, mediated solely via the H(4) R and via the combined action of H(2) R and H(4) R, respectively. In contrast, the production of IL-10 was not affected by histamine receptor activation on slanDC. The slanDC express the H(4) R and its stimulation leads to reduced pro-inflammatory capacity of slanDC. Hence, H(4) R agonists might have therapeutic potential to down-regulate immune reactions, e.g. in allergic inflammatory skin diseases.
Figures


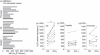
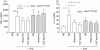
Similar articles
-
The histamine H4 receptor is highly expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells in psoriasis and histamine regulates their cytokine production and migration.J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Aug;131(8):1668-76. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.72. Epub 2011 May 26. J Invest Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21614010
-
Allergic inflammation is augmented via histamine H4 receptor activation: The role of natural killer cells in vitro and in vivo.J Dermatol Sci. 2016 Aug;83(2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Dermatol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27155791
-
Histamine downregulates monocyte CCL2 production through the histamine H4 receptor.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Aug;120(2):300-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.03.024. Epub 2007 May 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17507084
-
The role of the histamine H4 receptor in atopic dermatitis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011 Feb;11(1):21-8. doi: 10.1007/s11882-010-0162-7. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011. PMID: 21104170 Review.
-
The role of histamine H1 and H4 receptors in atopic dermatitis: from basic research to clinical study.Allergol Int. 2014 Dec;63(4):533-42. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.13-RA-0675. Allergol Int. 2014. PMID: 25249063 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the histamine H4 receptor in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;177(3):490-502. doi: 10.1111/bph.14550. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30460986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anaphylatoxin C5a Regulates 6-Sulfo-LacNAc Dendritic Cell Function in Human through Crosstalk with Toll-Like Receptor-Induced CREB Signaling.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 14;8:818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00818. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28769928 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of histamine and its receptors in atopic dermatitis.Mol Cell Pediatr. 2015 Dec;2(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40348-015-0027-1. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26690068 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine and neuroinflammation: insights from murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Front Syst Neurosci. 2012 May 3;6:32. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2012.00032. eCollection 2012. Front Syst Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22563309 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of histamine H4 receptor suppresses the proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via both metabolism and non-metabolism signaling pathways.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Sep;96(9):951-964. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1676-z. Epub 2018 Jul 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30058054
References
-
- Schakel K, Mayer E, Federle C, Schmitz M, Riethmuller G, Rieber EP. A novel dendritic cell population in human blood: one-step immunomagnetic isolation by a specific mAb (M-DC8) and in vitro priming of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:4084–93. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz M, Zhao S, Schakel K, Bornhauser M, Ockert D, Rieber EP. Native human blood dendritic cells as potent effectors in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Blood. 2002;100:1502–4. - PubMed
-
- Wehner R, Lobel B, Bornhauser M, et al. Reciprocal activating interaction between 6-sulfo LacNAc+ dendritic cells and NK cells. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:358–66. - PubMed
-
- Schakel K, von Kietzell M, Hansel A, et al. Human 6-sulfo LacNAc-expressing dendritic cells are principal producers of early interleukin-12 and are controlled by erythrocytes. Immunity. 2006;24:767–77. - PubMed
-
- Schakel K, Kannagi R, Kniep B, et al. 6-Sulfo LacNAc, a novel carbohydrate modification of PSGL-1, defines an inflammatory type of human dendritic cells. Immunity. 2002;17:289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

