Neuropeptide S stimulates dopaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 20722970
- PMCID: PMC2970681
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06947.x
Neuropeptide S stimulates dopaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex
Abstract
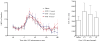
Neuropeptide S (NPS) is known to produce anxiolytic-like effects and facilitate extinction of conditioned fear. Catecholaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) has been suggested to be crucially involved in these brain functions. In the current study, we investigated the effect of NPS on the release of dopamine and serotonin in the mPFC by in vivo microdialysis in rats. Central administration of NPS dose-dependently enhanced extracellular levels of dopamine and its major metabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, with maximal effects lasting up to 120 min. In contrast, no effect on serotonergic neurotransmission was detected. Dopamine release in the mPFC has been previously linked to modulation of anxiety states and fear extinction. The present results may thus provide a physiological and anatomical basis for the reported effects of NPS on these behaviors.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal Compilation © 2010 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures
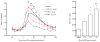
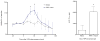
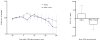
References
-
- Abercrombie ED, Keefe KA, DiFrischia DS, Zigmond MJ. Differential effect of stress on in vivo dopamine release in striatum, nucleus accumbens, and medial frontal cortex. J Neurochem. 1989;52:1655–1658. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G. Brain structures and receptors involved in alertness. Sleep Med. 2005;6 (Suppl 1):S3–S7. - PubMed
-
- Beaufour CC, Le Bihan C, Hamon M, Thiébot M. Extracellular dopamine in the rat prefrontal cortex during reward-, punishment- and novelty-associated behaviour. Effects of diazepam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 69:133–142. - PubMed
-
- Bonaventure P, Kelly L, Aluisio L, Shelton J, Lord B, Galici R, Miller K, Atack J, Lovenberg TW, Dugovic C. Selective blockade of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)7 receptors enhances 5-HT transmission, antidepressant-like behavior, and rapid eye movement sleep suppression induced by citalopram in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;321:690–698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

