JS-K has potent anti-angiogenic activity in vitro and inhibits tumour angiogenesis in a multiple myeloma model in vivo
- PMID: 20723011
- PMCID: PMC2925308
- DOI: 10.1211/jpp.62.01.0017
JS-K has potent anti-angiogenic activity in vitro and inhibits tumour angiogenesis in a multiple myeloma model in vivo
Abstract
Objectives: Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) play an important role in multidrug resistance and are upregulated in multiple cancers. We have designed a prodrug class that releases nitric oxide on metabolism by GST. O(2)-(2,4-Dinitrophenyl) 1-[(4-ethoxycarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate (JS-K, a member of this class) has potent antineoplastic activity.
Methods: We studied the effect of JS-K on angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), OPM1 multiple myeloma cells, chick aortic rings and in mice.
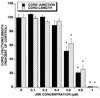
Key findings: JS-K inhibited the proliferation of HUVECs with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.432, 0.466 and 0.505 microm at 24, 48 and 72 h, respectively. In the cord formation assay, JS-K led to a decrease in the number of cord junctions and cord length with an IC50 of 0.637 and 0.696 microm, respectively. JS-K inhibited cell migration at 5 h using VEGF as a chemoattractant. Migration inhibition occurred with an IC50 of 0.493 microm. In the chick aortic ring assay using VEGF or FGF-2 for vessel growth stimulation, 0.5 microm JS-K completely inhibited vessel growth. JS-K inhibited tumour angiogenesis in vivo in NIH III mice implanted subcutaneously with OPM1 multiple myeloma cells.
Conclusions: JS-K is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis in vitro and tumour vessel growth in vivo. As such, it establishes a new class of antineoplastic agent that targets the malignant cells directly as well as their microenvironment.
Figures



References
-
- Magrinat G, Mason SN, Shami PJ, Weinberg JB. Nitric oxide modulation of human leukemia cell differentiation and gene expression. Blood. 1992;80:1880–1884. - PubMed
-
- Shami PJ, Moore JO, Gockerman JP, Hathorn JW, Misukonis MA, Weinberg JB. Nitric oxide modulation of the growth and differentiation of freshly isolated acute non-lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 1995;19:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Shami PJ, Sauls DL, Weinberg JB. Schedule and concentration-dependent induction of apoptosis in leukemia cells by nitric oxide. Leukemia. 1998;12:1461–1466. - PubMed
-
- Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991;43:109–142. - PubMed
-
- Shami PJ, Saavedra JE, Wang LY, Bonifant CL, Diwan BA, Singh SV, Gu Y, Fox SD, Buzard GS, Citro ML, Waterhouse DJ, Davies KM, Ji X, Keefer LK. JS-K, a Glutathione S-transferase-activated nitric oxide donor with potent anti-neoplastic activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:409–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

