Hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20723825
- PMCID: PMC2923455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2010.05.003
Hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
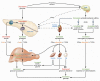
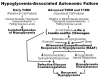
Iatrogenic hypoglycemia, typically the result of the interplay of therapeutic hyperinsulinemia and compromised defenses resulting in hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure (HAAF) in diabetes, is a problem for people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). It causes recurrent morbidity is sometimes fatal, leads to recurrent hypoglycemia, and precludes euglycemia over a lifetime of T1DM. Risk factors include those that result in relative or absolute insulin excess and those indicative of HAAF in diabetes. Elimination of hypoglycemia from the lives of people with T1DM will likely be accomplished by new treatment methods that provide plasma glucose-regulated insulin replacement or secretion.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cryer PE. Pathophysiology, Prevalence and Prevention. American Diabetes Association; Alexandria, VA: 2009. Hypoglycemia in Diabetes.
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60 DK20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK027085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK27085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK07120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

