Inhibition of Wnt signaling by Wise (Sostdc1) and negative feedback from Shh controls tooth number and patterning
- PMID: 20724449
- PMCID: PMC6512258
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.054668
Inhibition of Wnt signaling by Wise (Sostdc1) and negative feedback from Shh controls tooth number and patterning
Abstract
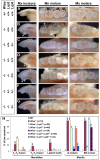
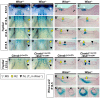
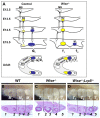
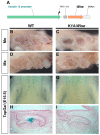
Mice carrying mutations in Wise (Sostdc1) display defects in many aspects of tooth development, including tooth number, size and cusp pattern. To understand the basis of these defects, we have investigated the pathways modulated by Wise in tooth development. We present evidence that, in tooth development, Wise suppresses survival of the diastema or incisor vestigial buds by serving as an inhibitor of Lrp5- and Lrp6-dependent Wnt signaling. Reducing the dosage of the Wnt co-receptor genes Lrp5 and Lrp6 rescues the Wise-null tooth phenotypes. Inactivation of Wise leads to elevated Wnt signaling and, as a consequence, vestigial tooth buds in the normally toothless diastema region display increased proliferation and continuous development to form supernumerary teeth. Conversely, gain-of-function studies show that ectopic Wise reduces Wnt signaling and tooth number. Our analyses demonstrate that the Fgf and Shh pathways are major downstream targets of Wise-regulated Wnt signaling. Furthermore, our experiments revealed that Shh acts as a negative-feedback regulator of Wnt signaling and thus determines the fate of the vestigial buds and later tooth patterning. These data provide insight into the mechanisms that control Wnt signaling in tooth development and into how crosstalk among signaling pathways controls tooth number and morphogenesis.
Figures
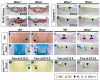
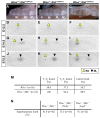
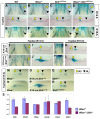
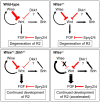
References
-
- Andl T., Reddy S. T., Gaddapara T., Millar S. E. (2002). WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev. Cell 2, 643-653. - PubMed
-
- Chiang C., Litingtung Y., Lee E., Young K. E., Corden J. L., Westphal H., Beachy P. A. (1996). Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature 383, 407-413. - PubMed
-
- Chu E. Y., Hens J., Andl T., Kairo A., Yamaguchi T. P., Brisken C., Glick A., Wysolmerski J. J., Millar S. E. (2004). Canonical WNT signaling promotes mammary placode development and is essential for initiation of mammary gland morphogenesis. Development 131, 4819-4829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

