Carbon monoxide promotes VEGF expression by increasing HIF-1alpha protein level via two distinct mechanisms, translational activation and stabilization of HIF-1alpha protein
- PMID: 20724477
- PMCID: PMC2952213
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.131284
Carbon monoxide promotes VEGF expression by increasing HIF-1alpha protein level via two distinct mechanisms, translational activation and stabilization of HIF-1alpha protein
Abstract
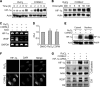
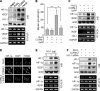
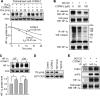
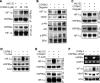
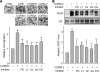
Carbon monoxide (CO) plays a significant role in vascular functions. We here examined the molecular mechanism by which CO regulates HIF-1 (hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1)-dependent expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is an important angiogenic factor. We found that astrocytes stimulated with CORM-2 (CO-releasing molecule) promoted angiogenesis by increasing VEGF expression and secretion. CORM-2 also induced HO-1 (hemeoxygenase-1) expression and increased nuclear HIF-1α protein level, without altering its promoter activity and mRNA level. VEGF expression was inhibited by treatment with HIF-1α siRNA and a hemeoxygenase inhibitor, indicating that CO stimulates VEGF expression via up-regulation of HIF-1α protein level, which is partially associated with HO-1 induction. CORM-2 activated the translational regulatory proteins p70(S6k) and eIF-4E as well as phosphorylating their upstream signal mediators Akt and ERK. These translational signal events and HIF-1α protein level were suppressed by inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), MEK, and mTOR, suggesting that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways are involved in a translational increase in HIF-1α. In addition, CORM-2 also increased stability of the HIF-1α protein by suppressing its ubiquitination, without altering the proline hydroxylase-dependent HIF-1α degradation pathway. CORM-2 increased HIF-1α/HSP90α interaction, which is responsible for HIF-1α stabilization, and HSP90-specific inhibitors decreased this interaction, HIF-1α protein level, and VEGF expression. Furthermore, HSP90α knockdown suppressed CORM-2-induced increases in HIF-1α and VEGF protein levels. These results suggest that CO stimulates VEGF production by increasing HIF-1α protein level via two distinct mechanisms, translational stimulation and protein stabilization of HIF-1α.
Figures

References
-
- Otterbein L. E., Zuckerbraun B. S., Haga M., Liu F., Song R., Usheva A., Stachulak C., Bodyak N., Smith R. N., Csizmadia E., Tyagi S., Akamatsu Y., Flavell R. J., Billiar T. R., Tzeng E., Bach F. H., Choi A. M., Soares M. P. (2003) Nat. Med. 9, 183–190 - PubMed
-
- Chauveau C., Bouchet D., Roussel J. C., Mathieu P., Braudeau C., Renaudin K., Tesson L., Soulillou J. P., Iyer S., Buelow R., Anegon I. (2002) Am. J. Transplant. 2, 581–592 - PubMed
-
- Foresti R., Bani-Hani M. G., Motterlini R. (2008) Intensive Care Med. 34, 649–658 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

