Novel role of C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP) ubiquitin ligase on inhibiting cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via regulating ERK5-mediated degradation of inducible cAMP early repressor
- PMID: 20724525
- PMCID: PMC2992371
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-162636
Novel role of C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP) ubiquitin ligase on inhibiting cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via regulating ERK5-mediated degradation of inducible cAMP early repressor
Abstract
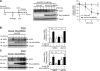
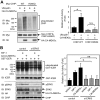
Growing evidence indicates a critical role of ubiquitin-proteosome system in apoptosis regulation. A cardioprotective effect of ubiquitin (Ub) ligase of the C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP) on myocytes has been reported. In the current study, we found that the cardioprotective effect of insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) was mediated by ERK5-CHIP signal module via inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) destabilization. In vitro runoff assay and Ub assay showed ICER as a substrate of CHIP Ub ligase. Both disruption of ERK5-CHIP binding with inhibitory helical linker domain fragment (aa 101-200) of CHIP and the depletion of ERK5 by siRNA inhibited CHIP Ub ligase activity, which suggests an obligatory role of ERK5 on CHIP activation. Depletion of CHIP, using siRNA, inhibited IGF-1-mediated reduction of isoproterenol-mediated ICER induction and apoptosis. In diabetic mice subjected to myocardial infarction, the CHIP Ub ligase activity was decreased, with an increase in ICER expression. These changes were attenuated significantly in a cardiac-specific constitutively active form of MEK5α transgenic mice (CA-MEK5α-Tg) previously shown to have greater functional recovery. Furthermore, pressure overload-mediated ICER induction was enhanced in heterozygous CHIP(+/-) mice. We identified ICER as a novel CHIP substrate and that the ERK5-CHIP complex plays an obligatory role in inhibition of ICER expression, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and cardiac dysfunction.
Figures
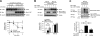

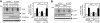


Similar articles
-
p90RSK targets the ERK5-CHIP ubiquitin E3 ligase activity in diabetic hearts and promotes cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction.Circ Res. 2012 Feb 17;110(4):536-50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.254730. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22267842 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 reduces cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via inhibition of a phosphodiesterase 3A/inducible cAMP early repressor feedback loop.Circ Res. 2007 Mar 2;100(4):510-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000259045.49371.9c. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17272811 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of MEK5/ERK5 association on small ubiquitin-related modification of ERK5: implications for diabetic ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Circ Res. 2008 Jun 6;102(11):1416-25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.168138. Epub 2008 May 8. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18467627 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 21;6:28399. doi: 10.1038/srep28399. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27323684 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Potential of Exogenous Ubiquitin.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021 Dec;35(6):1227-1232. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07042-5. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021. PMID: 32910339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Decade of Boon or Burden: What Has the CHIP Ever Done for Cellular Protein Quality Control Mechanism Implicated in Neurodegeneration and Aging?Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Oct 4;9:93. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00093. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27757073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CHIP Is an Essential Determinant of Neuronal Mitochondrial Stress Signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Aug 20;23(6):535-49. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6102. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25602369 Free PMC article.
-
An update of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase as a target for cardiac diseases.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021 Feb;16(2):183-196. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1821643. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 32957823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that the transcriptional repressor ICER is regulated via the N-end rule for ubiquitination.Exp Cell Res. 2022 May 1;414(1):113083. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113083. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 35227662 Free PMC article.
-
CHIP: A new modulator of human malignant disorders.Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):29864-74. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8219. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27007160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomita H., Nazmy M., Kajimoto K., Yehia G., Molina C. A., Sadoshima J. (2003) Inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) is a negative-feedback regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and an important mediator of cardiac myocyte apoptosis in response to beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Circ. Res. 93, 12–22 - PubMed
-
- Ding B., Abe J., Wei H., Xu H., Che W., Aizawa T., Liu W., Molina C. A., Sadoshima J., Blaxall B. C., Berk B. C., Yan C. (2005) A positive feedback loop of phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) and inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 14771–14776 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akaike M., Che W., Marmarosh N. L., Ohta S., Osawa M., Ding B., Berk B. C., Yan C., Abe J. (2004) The hinge-helix 1 region of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 (PPARgamma1) mediates interaction with extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 and PPARgamma1 transcriptional activation: involvement in flow-induced PPARgamma activation in endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 8691–8704 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yan C., Ding B., Shishido T., Woo C. H., Itoh S., Jeon K. I., Liu W., Xu H., McClain C., Molina C. A., Blaxall B. C., Abe J. (2007) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 reduces cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via inhibition of a phosphodiesterase 3A/inducible cAMP early repressor feedback loop. Circ. Res. 100, 510–519 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

