Olfactomedin 4 is a novel target gene of retinoic acids and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine involved in human myeloid leukemia cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis
- PMID: 20724538
- PMCID: PMC3012588
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-246439
Olfactomedin 4 is a novel target gene of retinoic acids and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine involved in human myeloid leukemia cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis
Abstract
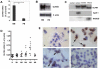
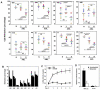
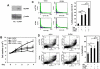
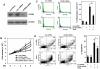
Clinical application of retinoic acids (RAs) and demethylation agents has proven to be effective in treating certain myeloid leukemia patients. However, the target genes that mediate these antileukemia activities are still poorly understood. In this study, we identified olfactomedin 4 (OLFM4), a myeloid-lineage-specific gene from the olfactomedin family, as a novel target gene for RAs and the demethylation agent, 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine. We demonstrated that the retinoic acid receptor alpha/retinoic X receptor alpha heterodimer binds to a retinoic acid response-element (DR5) site in the OLFM4 promoter and mediates all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced transactivation of the OLFM4 gene. OLFM4 overexpression in HL-60 cells led to growth inhibition, differentiation, and apoptosis, and potentiated ATRA induction of these effects. Conversely, down-regulation of endogenous OLFM4 in acute myeloid leukemia-193 cells compromised ATRA-induced growth inhibition, differentiation, and apoptosis. Overexpression of OLFM4 in HL-60 cells inhibited constitutive and ATRA-induced phosphorylation of the eukaryote initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), whereas down-regulation of OLFM4 protein in acute myeloid leukemia-193 cells increased 4E-BP1 phosphorylation, suggesting that OLFM4 is a potent upstream inhibitor of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation/deactivation. Thus, our study demonstrates that OLFM4 plays an important role in myeloid leukemia cellular functions and induction of OLFM4-mediated effects may contribute to the therapeutic value of ATRA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The oncogene EVI1 enhances transcriptional and biological responses of human myeloid cells to all-trans retinoic acid.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2931-43. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.946869. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486480 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid receptor-β gene reexpression and biological activity in SHI-1 cells after combined treatment with 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and all-trans retinoic acid.Acta Haematol. 2015;133(3):279-86. doi: 10.1159/000367586. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Acta Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25413479
-
[Epigenetic regulation of expression of retinoic acid receptor beta gene in leukemia cell].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Dec 25;87(48):3406-10. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18476539 Chinese.
-
MicroRNA and DNA methylation alterations mediating retinoic acid induced neuroblastoma cell differentiation.Semin Cancer Biol. 2011 Oct;21(4):283-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011. PMID: 21771658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Differentiation induction of leukemia cells].Rinsho Ketsueki. 1998 Jan;39(1):6-7. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1998. PMID: 9492548 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial gene expression signature predicts prognosis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;13:1109518. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1109518. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845715 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactomedin 4 contributes to hydrogen peroxide-induced NADPH oxidase activation and apoptosis in mouse neutrophils.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):C494-C501. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00336.2017. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29949402 Free PMC article.
-
Differential proteomic analysis of virus-enriched fractions obtained from plasma pools of patients with dengue fever or severe dengue.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 14;15:518. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1271-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26572220 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially-expressed of Olfactomedin-related proteins 4 and COL11A1 in Iranian patients with intestinal gastric cancer.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2017 Winter;10(Suppl1):S62-S69. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2017. PMID: 29511474 Free PMC article.
-
Novel quinazolinone MJ-29 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and intrinsic apoptosis in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells and inhibits leukemic mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036831. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, et al. Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988;72(2):567–572. - PubMed
-
- Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, et al. All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia: long-term outcome and prognostic factor analysis from the North American Intergroup protocol. Blood. 2002;100(13):4298–4302. - PubMed
-
- Lubbert M. DNA methylation inhibitors in the treatment of leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, and hemoglobinopathies: clinical results and possible mechanisms of action. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;249:135–164. - PubMed
-
- Soriano AO, Yang H, Faderl S, et al. Safety and clinical activity of the combination of 5-azacytidine, valproic acid, and all-trans retinoic acid in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 2007;110(7):2302–2308. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Liu WL, Tang DC, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel member of olfactomedin-related protein family, hGC-1, expressed during myeloid lineage development. Gene. 2002;283(1-2):83–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

