Monocyte-bound PF4 in the pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 20724543
- PMCID: PMC3012595
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276964
Monocyte-bound PF4 in the pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Abstract
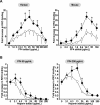
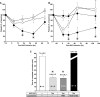
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a life- and limb-threatening thrombotic disorder that develops after exposure to heparin, often in the setting of inflammation. We have shown previously that HIT is associated with antibodies to complexes that form between platelet factor 4 and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) side chains on the surface of platelets. However, thrombosis can occur in the absence of thrombocytopenia. We now show that platelet factor 4 binds to monocytes and forms antigenic complexes with their surface GAG side chains more efficiently than on platelets likely due to differences in GAG composition. Binding to monocytes is enhanced when the cells are activated by endotoxin. Monocyte accumulation within developing arteriolar thrombi was visualized by situ microscopy. Monocyte depletion or inactivation in vivo attenuates thrombus formation induced by photochemical injury of the carotid artery in a modified murine model of HIT while paradoxically exacerbating thrombocytopenia. These studies demonstrate a previously unappreciated role for monocytes in the pathogenesis of arterial thrombosis in HIT and suggest that therapies targeting these cells might provide an alternative approach to help limit thrombosis in this and possibly other thrombotic disorders that occur in the setting of inflammation.
Figures

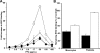
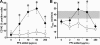
References
-
- Loscalzo J, Melnick B, Handin RI. The interaction of platelet factor four and glycosaminoglycans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985;240(1):446–455. - PubMed
-
- George JN, Onofre AR. Human platelet surface binding of endogenous secreted factor VIII-von Willebrand factor and platelet factor 4. Blood. 1982;59(1):194–197. - PubMed
-
- Rao AK, Niewiarowski S, James P, et al. Effect of heparin on the in vivo release and clearance of human platelet factor 4. Blood. 1983;61(6):1208–1214. - PubMed
-
- Amiral J, Bridey F, Dreyfus M, et al. Platelet factor 4 complexed to heparin is the target for antibodies generated in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 1992;68(1):95–96. - PubMed
-
- Greinacher A, Potzsch B, Amiral J, Dummel V, Eichner A, Mueller-Eckhardt C. Heparin-associated thrombocytopenia: isolation of the antibody and characterization of a multimolecular PF4-heparin complex as the major antigen. Thromb Haemost. 1994;71(2):247–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

