Lack of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in CD3+ lymphocytes leads to aberrant cytokine secretion and hyperinflammatory adaptive immune responses
- PMID: 20724552
- PMCID: PMC3135852
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0224OC
Lack of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in CD3+ lymphocytes leads to aberrant cytokine secretion and hyperinflammatory adaptive immune responses
Abstract
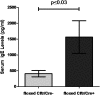
Cystic fibrosis (CF), the most common fatal monogenic disease in the United States, results from mutations in CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a chloride channel. The mechanisms by which CFTR mutations cause lung disease in CF are not fully defined but may include altered ion and water transport across the airway epithelium and aberrant inflammatory and immune responses to pathogens within the airways. We have shown that Cftr(-/-) mice mount an exaggerated IgE response toward Aspergillus fumigatus, with higher levels of IL-13 and IL-4, mimicking both the T helper cell type 2-biased immune responses seen in patients with CF. Herein, we demonstrate that these aberrations are primarily due to Cftr deficiency in lymphocytes rather than in the epithelium. Adoptive transfer experiments with CF splenocytes confer a higher IgE response to Aspergillus fumigatus compared with hosts receiving wild-type splenocytes. The predilection of Cftr-deficient lymphocytes to mount T helper cell type 2 responses with high IL-13 and IL-4 was confirmed by in vitro antigen recall experiments. Conclusive data on this phenomenon were obtained with conditional Cftr knockout mice, where mice lacking Cftr in T cell lineages developed higher IgE than their wild-type control littermates. Further analysis of Cftr-deficient lymphocytes revealed an enhanced intracellular Ca(2+) flux in response to T cell receptor activation. This was accompanied by an increase in nuclear localization of the calcium-sensitive transcription factor, nuclear factor of activated T cell, which could drive the IL-13 response. In summary, our data identified that CFTR dysfunction in T cells can lead directly to aberrant immune responses. These findings implicate the lymphocyte population as a potentially important target for CF therapeutics.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator regulates epithelial cell response to Aspergillus and resultant pulmonary inflammation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Feb 1;185(3):301-10. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201106-1027OC. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22135344 Free PMC article.
-
Partial correction of the CFTR-dependent ABPA mouse model with recombinant adeno-associated virus gene transfer of truncated CFTR gene.J Gene Med. 2008 Jan;10(1):51-60. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1119. J Gene Med. 2008. PMID: 18023072
-
mGluR1 interacts with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and modulates the secretion of IL-10 in cystic fibrosis peripheral lymphocytes.Mol Immunol. 2012 Jul;51(3-4):310-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.03.029. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22520513
-
The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Receptor Brakes Allergic Airway Inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2025 Mar;330(1):e70009. doi: 10.1111/imr.70009. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39981881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse models of chronic lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: models for the study of cystic fibrosis.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000 Nov;30(5):413-24. doi: 10.1002/1099-0496(200011)30:5<413::aid-ppul8>3.0.co;2-9. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000. PMID: 11064433 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium, Phosphorus, and Vitamin D Levels in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1900. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031900. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339178 Free PMC article.
-
Super resolution microscopy analysis reveals increased Orai1 activity in asthma and cystic fibrosis lungs.J Cyst Fibros. 2023 Jan;22(1):161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2022.07.003. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Cyst Fibros. 2023. PMID: 35961837 Free PMC article.
-
A Link Between a Common Mutation in CFTR and Impaired Innate and Adaptive Viral Defense.J Infect Dis. 2017 Dec 5;216(10):1308-1317. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix474. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28968805 Free PMC article.
-
Elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor use after solid organ transplant.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2024 Nov 1;30(6):660-666. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000001110. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39082904 Review.
-
Type 2 inflammation in cystic fibrosis is a predictor of mortality and targeted with CFTR modulator therapy.Allergy. 2024 Dec;79(12):3528-3533. doi: 10.1111/all.16198. Epub 2024 Jun 16. Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38881035 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wainwright B. The molecular pathology of cystic fibrosis. Curr Biol 1991;1:80–82. - PubMed
-
- Davidson DJ, Webb S, Teague P, Govan JR, Dorin JR. Lung pathology in response to repeated exposure to Staphylococcus aureus in congenic residual function cystic fibrosis mice does not increase in response to decreased CFTR levels or increased bacterial load. Pathobiology 2004;71:152–158. - PubMed
-
- Pier GB. CFTR mutations and host susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 2002;5:81–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

