Pharmacological vasodilation improves insulin-stimulated muscle protein anabolism but not glucose utilization in older adults
- PMID: 20724580
- PMCID: PMC2963534
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0415
Pharmacological vasodilation improves insulin-stimulated muscle protein anabolism but not glucose utilization in older adults
Abstract
Objective: Skeletal muscle protein metabolism is resistant to the anabolic action of insulin in healthy, nondiabetic older adults. This defect is associated with impaired insulin-induced vasodilation and mTORC1 signaling. We hypothesized that, in older subjects, pharmacological restoration of insulin-induced capillary recruitment would improve the response of muscle protein synthesis and anabolism to insulin.
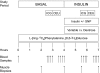
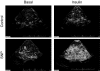
Research design and methods: Twelve healthy, nondiabetic older subjects (71 ± 2 years) were randomized to two groups. Subjects were studied at baseline and during local infusion in one leg of insulin alone (Control) or insulin plus sodium nitroprusside (SNP) at variable rate to double leg blood flow. We measured leg blood flow by dye dilution; muscle microvascular perfusion with contrast enhanced ultrasound; Akt/mTORC1 signaling by Western blotting; and muscle protein synthesis, amino acid, and glucose kinetics using stable isotope methodologies.
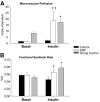
Results: There were no baseline differences between groups. Blood flow, muscle perfusion, phenylalanine delivery to the leg, and intracellular availability of phenylalanine increased significantly (P < 0.05) in SNP only. Akt phosphorylation increased in both groups but increased more in SNP (P < 0.05). Muscle protein synthesis and net balance (nmol · min(-1) · 100 ml · leg(-1)) increased significantly (P < 0.05) in SNP (synthesis, 43 ± 6 to 129 ± 25; net balance, -16 ± 3 to 26 ± 12) but not in Control (synthesis, 41 ± 10 to 53 ± 8; net balance, -17 ± 3 to -2 ± 3).
Conclusions: Pharmacological enhancement of muscle perfusion and amino acid availability during hyperinsulinemia improves the muscle protein anabolic effect of insulin in older adults.
Figures


References
-
- Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Lee JS, Kuller LH, Boudreau R, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Kritchevsky S, Tylavsky FA, Nevitt M, Cho YW, Newman ABHealth, Aging, and Body Composition Study Excessive loss of skeletal muscle mass in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1993–1997 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennet WM, Connacher AA, Scrimgeour CM, Jung RT, Rennie MJ. Euglycemic hyperinsulinemia augments amino acid uptake by human leg tissues during hyperaminoacidemia. Am J Physiol 1990;259:E185–E194 - PubMed
-
- Bennet WM, Rennie MJ. Protein anabolic actions of insulin in the human body. Diabet Med 1991;8:199–207 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

