Genetic ablation of TWEAK augments regeneration and post-injury growth of skeletal muscle in mice
- PMID: 20724600
- PMCID: PMC2947270
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100335
Genetic ablation of TWEAK augments regeneration and post-injury growth of skeletal muscle in mice
Abstract
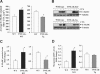
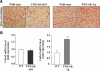
Impairment in the regeneration process is a critical determinant for skeletal muscle wasting in chronic diseases and degenerative muscle disorders. Inflammatory cytokines are known to cause significant muscle wasting, however, their role in myofiber regeneration is less clear. In this study we have investigated the role of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) in skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo. Our results show that expression levels of TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 are significantly increased in skeletal muscles of mice after injury. Genetic deletion of TWEAK increased the fiber cross-sectional area and levels of embryonic isoform of myosin heavy chain in regenerating tibial anterior muscle. Conversely, muscle-specific transgenic overexpression of TWEAK reduced the fiber cross-sectional area and levels of the embryonic myosin heavy chain in regenerating muscle. TWEAK induced the expression of several inflammatory molecules and increased interstitial fibrosis in regenerating muscle. Genetic ablation of TWEAK suppressed, whereas overexpression of TWEAK increased, the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B without affecting the activation of Akt or p38 kinase in regenerating myofibers. Primary myoblasts from TWEAK-null mice showed enhanced differentiation in vitro, whereas myoblasts from TWEAK-Tg mice showed reduced differentiation compared with wild-type mice. Collectively, our study suggests that TWEAK negatively regulates muscle regeneration and that TWEAK is a potential therapeutic target to enhance skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo.
Figures


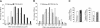



Similar articles
-
Elevated levels of TWEAK in skeletal muscle promote visceral obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic dysfunction.FASEB J. 2015 Mar;29(3):988-1002. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-260703. Epub 2014 Dec 2. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25466899 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) activates proinflammatory signaling pathways and gene expression through the activation of TGF-beta-activated kinase 1.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2439-48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803357. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19201899 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK, via its receptor Fn14, is a novel regulator of mesenchymal progenitor cells and skeletal muscle regeneration.EMBO J. 2006 Dec 13;25(24):5826-39. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601441. Epub 2006 Nov 23. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 17124496 Free PMC article.
-
The TWEAK-Fn14 system: breaking the silence of cytokine-induced skeletal muscle wasting.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jan;12(1):3-13. doi: 10.2174/156652412798376107. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22082477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TWEAK-Fn14 pathway: a potent regulator of skeletal muscle biology in health and disease.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Apr;25(2):215-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 24444596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated levels of TWEAK in skeletal muscle promote visceral obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic dysfunction.FASEB J. 2015 Mar;29(3):988-1002. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-260703. Epub 2014 Dec 2. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25466899 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-inducible 14 (Fn14) for tumor therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 21;13:935086. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.935086. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TWEAK-Fn14 system as a potential drug target.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;170(4):748-64. doi: 10.1111/bph.12337. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23957828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine expression and cytokine-mediated cell-cell communication during skeletal muscle regeneration revealed by integrative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 4;18(4):e12055. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12055. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39691872 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TWEAK in lupus nephritis: a bench-to-bedside review.J Autoimmun. 2012 Sep;39(3):130-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Autoimmun. 2012. PMID: 22727560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charge SB, Rudnicki MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:209–238. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan J, Rando TA. Stem cells in postnatal myogenesis: molecular mechanisms of satellite cell quiescence, activation and replenishment. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:666–673. - PubMed
-
- Relaix F, Marcelle C. Muscle stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:748–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

