Polyubiquitin conjugation to NEMO by triparite motif protein 23 (TRIM23) is critical in antiviral defense
- PMID: 20724660
- PMCID: PMC2936632
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1004621107
Polyubiquitin conjugation to NEMO by triparite motif protein 23 (TRIM23) is critical in antiviral defense
Abstract
The rapid induction of type I IFN is a central event of the innate defense against viral infections and is tightly regulated by a number of cellular molecules. Viral components induce strong type I IFN responses through the activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs) and intracellular cytoplasmic receptors such as an RNA helicase RIG-I and/or MDA5. According to recent studies, the NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO, also called IKKgamma) is crucial for this virus-induced antiviral response. However, the precise roles of signal activation by NEMO adaptor have not been elucidated. Here, we show that virus-induced IRF3 and NF-kappaB activation depends on the K(lys)-27-linked polyubiquitination to NEMO by the novel ubiquitin E3 ligase triparite motif protein 23 (TRIM23). Virus-induced IRF3 and NF-kappaB activation, as well as K27-linked NEMO polyubiquitination, were abrogated in TRIM23 knockdown cells, whereas TRIM23 knockdown had no effect on TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Furthermore, in NEMO-deficient mouse embryo fibroblast cells, IFN-stimulated response element-driven reporter activity was restored by ectopic expression of WT NEMO, as expected, but only partial recovery by NEMO K165/309/325/326/344R multipoints mutant on which TRIM23-mediated ubiquitin conjugation was substantially reduced. Thus, we conclude that TRIM23-mediated ubiquitin conjugation to NEMO is essential for TLR3- and RIG-I/MDA5-mediated antiviral innate and inflammatory responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
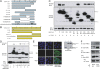

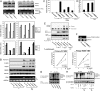
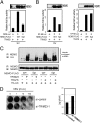
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Honda K, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T. Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity. 2006;25:349–360. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity. 2006;25:373–381. - PubMed
-
- Meylan E, Tschopp J, Karin M. Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response. Nature. 2006;442:39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

