Plasma renin activity predicts blood pressure responses to beta-blocker and thiazide diuretic as monotherapy and add-on therapy for hypertension
- PMID: 20725057
- PMCID: PMC2941699
- DOI: 10.1038/ajh.2010.98
Plasma renin activity predicts blood pressure responses to beta-blocker and thiazide diuretic as monotherapy and add-on therapy for hypertension
Abstract
Background: Age and race categories or renin profiling have been recommended to predict blood pressure responses to monotherapy with a beta-blocker or thiazide diuretic. Whether these or other characteristics predict blood pressure responses when the drugs are administered as add-on therapy is uncertain.
Methods: We evaluated predictors of blood pressure response in 363 men and women < or =65 years of age with primary hypertension (152 blacks, 211 whites), 86 of whom (24%) were untreated and 277 of whom (76%) were withdrawn from previous antihypertensive drugs before randomization to either atenolol followed by addition of hydrochlorothiazide (N = 180) or hydrochlorothiazide followed by addition of atenolol (N = 183). Responses were determined by home blood pressure averages before and after each drug administration. Race, age, plasma renin activity, and other characteristics including pretreatment blood pressure levels were incorporated into linear regression models to quantify their contributions to prediction of blood pressure responses.
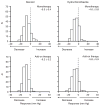
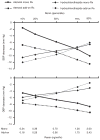
Results: Plasma renin activity and pretreatment blood pressure level consistently contributed to prediction of systolic and diastolic responses to each drug administered as mono- and as add-on therapy. Higher plasma renin activity was consistently associated with greater blood pressure responses to atenolol and lesser responses to hydrochlorothiazide. The predictive effects of plasma renin activity were statistically independent of race, age, and other characteristics.
Conclusions: Plasma renin activity and pretreatment blood pressure level predict blood pressure responses to atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide administered as mono- and as add-on therapy in men and women < or =65 years of age.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Heterogeneity of blood pressure response to therapy.Am J Hypertens. 2010 Sep;23(9):926-8. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2010.139. Am J Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20733564 No abstract available.
-
Renin-guided treatment of hypertension: time for action.Am J Hypertens. 2010 Sep;23(9):929-30. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2010.135. Am J Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20733565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Freis ED, Materson BJ, Flamenbaum V. Comparison of propranolol or hydrochlorothiazide alone for treatment of hypertension. III. Evaluation of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Med. 1983;74:1029–1041. - PubMed
-
- Bidiville J, Nussberger J, Waeber G, Porchet M, Waeber B, Brunner HR. Individual responses to converting enzyme inhibitors and calcium antagonists. Hypertension. 1988;11:166–173. - PubMed
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, Hamburger RJ, Fye C, Lakshman R, Gottdiener J. Single-drug therapy for hypertension in men. A comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. The Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:914–921. - PubMed
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Preston RA, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, Hamburger RJ, Fye C, Lakshman R. Response to a second single antihypertensive agent used as monotherapy for hypertension after failure of the initial drug. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:1757–1762. - PubMed
-
- Dickerson JE, Hingorani AD, Ashby MJ, Palmer CR, Brown MJ. Optimisation of antihypertensive treatment by crossover rotation of four major classes. Lancet. 1999;353:2008–2013. - PubMed

