Role of nicotinamide in DNA damage, mutagenesis, and DNA repair
- PMID: 20725615
- PMCID: PMC2915624
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/157591
Role of nicotinamide in DNA damage, mutagenesis, and DNA repair
Abstract
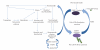
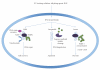
Nicotinamide is a water-soluble amide form of niacin (nicotinic acid or vitamin B3). Both niacin and nicotinamide are widely available in plant and animal foods, and niacin can also be endogenously synthesized in the liver from dietary tryptophan. Nicotinamide is also commercially available in vitamin supplements and in a range of cosmetic, hair, and skin preparations. Nicotinamide is the primary precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)), an essential coenzyme in ATP production and the sole substrate of the nuclear enzyme poly-ADP-ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have clearly shown that PARP-1 and NAD(+) status influence cellular responses to genotoxicity which can lead to mutagenesis and cancer formation. This paper will examine the role of nicotinamide in the protection from carcinogenesis, DNA repair, and maintenance of genomic stability.
Figures
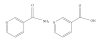
References
-
- Jacob RA, Swendseid ME. Niacin. In: Ziegler EE, Filer LJ, editors. Present Knowledge in Nutrition. Washington, DC, USA: ILSI Press; 1996. pp. 184–190.
-
- Benavente CA, Jacobson MK, Jacobson EL. NAD in skin: therapeutic approaches for niacin. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2009;15(1):29–38. - PubMed
-
- Karthikeyan K, Thappa DM. Pellagra and skin. International Journal of Dermatology. 2002;41(8):476–481. - PubMed
-
- Nutrient Reference Values for Australian and New Zealand, including recommended dietary intake. pp.1–329, National Health and Medical Research Council publication, Canberra, Australia, 2006.
-
- Jackson TM, Rawling JM, Roebuck BD, Kirkland JB. Large supplements of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide increase tissue NAD+ and poly(ADP-ribose) levels but do not affect diethylnitrosamine-induced altered hepatic foci in Fischer-344 rats. Journal of Nutrition. 1995;125(6):1455–1461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

