Synthesis and g-quadruplex-binding properties of defined acridine oligomers
- PMID: 20725626
- PMCID: PMC2915818
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/489060
Synthesis and g-quadruplex-binding properties of defined acridine oligomers
Abstract
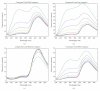
The synthesis of oligomers containing two or three acridine units linked through 2-aminoethylglycine using solid-phase methodology is described. Subsequent studies on cell viability showed that these compounds are not cytotoxic. Binding to several DNA structures was studied by competitive dialysis, which showed a clear affinity for DNA sequences that form G-quadruplexes and parallel triplexes. The fluorescence spectra of acridine oligomers were affected strongly upon binding to DNA. These spectral changes were used to calculate the binding constants (K). Log K were found to be in the order of 4-6.
Figures

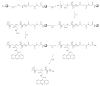

References
-
- Palchaudhuri R, Hergenrother PJ. DNA as a target for anticancer compounds: methods to determine the mode of binding and the mechanism of action. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2007;18(6):497–503. - PubMed
-
- Parkinson GN, Lee MPH, Neidle S. Crystal structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA. Nature. 2002;417(6891):876–880. - PubMed
-
- Huppert JL. Hunting G-quadruplexes. Biochimie. 2008;90(8):1140–1148. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

