Polymeric micelles in anticancer therapy: targeting, imaging and triggered release
- PMID: 20725771
- PMCID: PMC2982955
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0233-4
Polymeric micelles in anticancer therapy: targeting, imaging and triggered release
Abstract
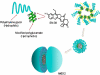
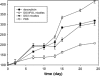
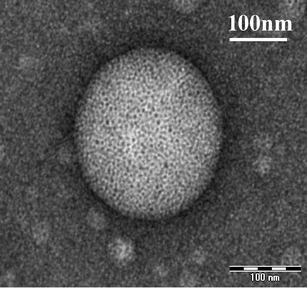
Micelles are colloidal particles with a size around 5-100 nm which are currently under investigation as carriers for hydrophobic drugs in anticancer therapy. Currently, five micellar formulations for anticancer therapy are under clinical evaluation, of which Genexol-PM has been FDA approved for use in patients with breast cancer. Micelle-based drug delivery, however, can be improved in different ways. Targeting ligands can be attached to the micelles which specifically recognize and bind to receptors overexpressed in tumor cells, and chelation or incorporation of imaging moieties enables tracking micelles in vivo for biodistribution studies. Moreover, pH-, thermo-, ultrasound-, or light-sensitive block copolymers allow for controlled micelle dissociation and triggered drug release. The combination of these approaches will further improve specificity and efficacy of micelle-based drug delivery and brings the development of a 'magic bullet' a major step forward.
Figures
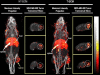
References
-
- World Health Organization: fact sheet cancer. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/index.html. (accessed 10-12-09).
-
- Mishra B, Patel BB, Tiwari S. Colloidal nanocarriers: a review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Nanomedicine. 2010;6:9–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

