Tumor expression of B7-H4 predicts poor survival of patients suffering from gastric cancer
- PMID: 20725832
- PMCID: PMC11031090
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0900-7
Tumor expression of B7-H4 predicts poor survival of patients suffering from gastric cancer
Abstract
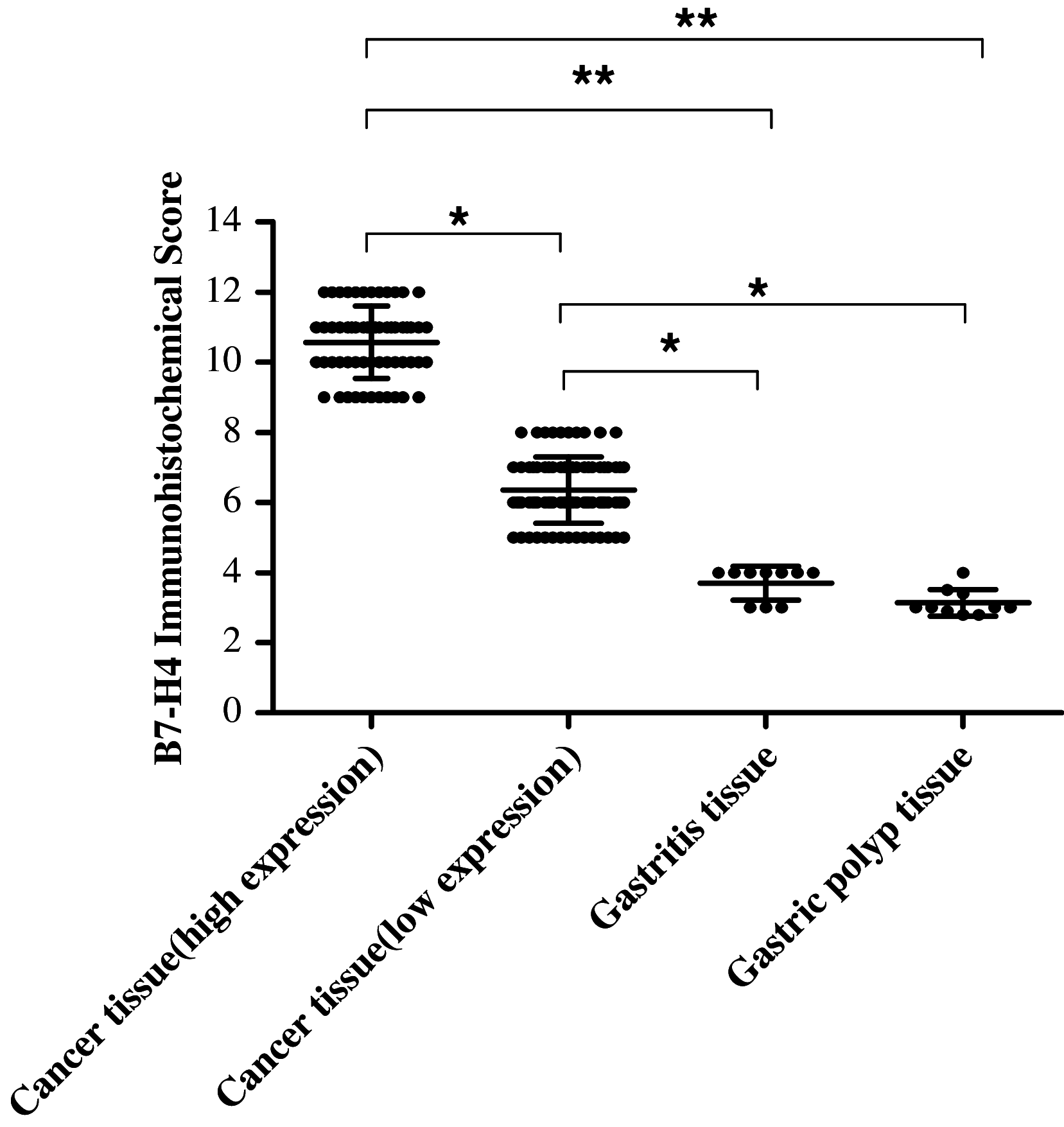
To establish the prognostic value of B7-H4 expression by tumor cells in gastric cancer patients, we evaluated the association of B7-H4 expression with clinicopathologic factors and overall survival of gastric cancer patients. A retrospective cohort study including 156 gastric cancer patients was performed in the present report. Immunohistochemical assay was used to evaluate the expression of B7-H4 in the surgical specimens of gastric cancer tissues. Multi-univariate COX model was then used to evaluate the association of B7-H4 expression with the patients' survival and clinicopathological parameters. B7-H4 expression in the gastric cancer cells was observed in about 44.9% gastric cancer specimens. Univariate analysis demonstrated that there was no correlation between B7-H4 expression and sex, age, histological type, pathological grade or tumor size. In contrast, B7-H4 expression correlated positively with cancer invasiveness and lymph node metastasis. In addition, the median overall survival time of patients with lower B7-H4 expression was 13 months longer than that of patients with higher expression (chi(2) = 12.38, P < 0.0001), and the median disease-free survival time of patients with lower B7-H4 expression was significantly longer than that of patients with higher expression (33 vs. 16 months, chi(2) = 14.977, P < 0.0001). After adjustment for other confounding factors, the COX model analysis indicated that the death risk was significantly higher in patients with higher B7-H4 expression than those with lower expression (RR = 1.85, 95% CI = 1.15-2.96). The present study demonstrated that higher B7-H4 expression in cancer cells was associated with poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients. This is consistent with the idea that B7-H4 promotes cancer progression, likely via inhibition of anti-tumor immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing or financial interests regarding this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
B7-H4 expression associates with cancer progression and predicts patient's survival in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Jul;60(7):1047-55. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1017-3. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21519829 Free PMC article.
-
Serum B7-H4 expression is a significant prognostic indicator for patients with gastric cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2014 Jun 19;12:188. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-188. World J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24947047 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of costimulatory molecules B7-H1, B7-H4 and Foxp3+ Tregs in gastric cancer and its clinical significance.Int J Clin Oncol. 2015 Apr;20(2):273-81. doi: 10.1007/s10147-014-0701-7. Epub 2014 May 9. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 24804867
-
Clinical significance of the B7-H4 coregulatory molecule as a novel prognostic marker in gastric cancer.World J Surg. 2011 Sep;35(9):2051-7. doi: 10.1007/s00268-011-1186-4. World J Surg. 2011. PMID: 21748517
-
Could B7-H4 serve as a target to activate anti-cancer immunity?Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Sep;38:97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.05.020. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27258187 Review.
Cited by
-
B7-H3 as a Target for CAR-T Cell Therapy in Skull Base Chordoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 15;11:659662. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.659662. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34868903 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of tumor response to cytokine-induced killer cells therapy in malignant solid tumors.J Transl Med. 2014 Aug 12;12:215. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0215-0. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25113800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: beyond CTLA-4 and PD-1.Immunotherapy. 2015;7(11):1169-86. doi: 10.2217/imt.15.78. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Immunotherapy. 2015. PMID: 26567614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of soluble H7-B4 in pleural effusion associated with lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4397-403. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3079-x. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25636447
-
Prognostic significance of B7-H4 expression in matched primary pancreatic cancer and liver metastases.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):72242-72249. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12665. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27750217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valentini V, Cellini F, Minsky BD, Mattiucci GC, Balducci M, D’Agostino G, D’Angelo E, Dinapoli N, Nicolotti N, Valentini C, La Torre G. Survival after radiotherapy in gastric cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:176–183. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.06.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

