Using electron beam radiation to simulate the dose distribution for whole body solar particle event proton exposure
- PMID: 20725839
- PMCID: PMC3575686
- DOI: 10.1007/s00411-010-0315-z
Using electron beam radiation to simulate the dose distribution for whole body solar particle event proton exposure
Abstract
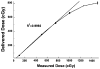
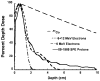
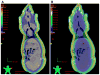
As a part of the near solar system exploration program, astronauts may receive significant total body proton radiation exposures during a solar particle event (SPE). In the Center for Acute Radiation Research (CARR), symptoms of the acute radiation sickness syndrome induced by conventional radiation are being compared to those induced by SPE-like proton radiation, to determine the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of SPE protons. In an SPE, the astronaut's whole body will be exposed to radiation consisting mainly of protons with energies below 50 MeV. In addition to providing for a potentially higher RBE than conventional radiation, the energy distribution for an SPE will produce a relatively inhomogeneous total body dose distribution, with a significantly higher dose delivered to the skin and subcutaneous tissues than to the internal organs. These factors make it difficult to use a (60)Co standard for RBE comparisons in our experiments. Here, the novel concept of using megavoltage electron beam radiation to more accurately reproduce both the total dose and the dose distribution of SPE protons and make meaningful RBE comparisons between protons and conventional radiation is described. In these studies, Monte Carlo simulation was used to determine the dose distribution of electron beam radiation in small mammals such as mice and ferrets as well as large mammals such as pigs. These studies will help to better define the topography of the time-dose-fractionation versus biological response landscape for astronaut exposure to an SPE.
Figures
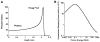

Similar articles
-
Acute biological effects of simulating the whole-body radiation dose distribution from a solar particle event using a porcine model.Radiat Res. 2011 Nov;176(5):649-59. doi: 10.1667/rr2541.1. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Radiat Res. 2011. PMID: 21859326 Free PMC article.
-
Dermatopathology effects of simulated solar particle event radiation exposure in the porcine model.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2015 Jul;6:21-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2015. PMID: 26256624 Free PMC article.
-
Relative biological effectiveness of simulated solar particle event proton radiation to induce acute hematological change in the porcine model.J Radiat Res. 2014 Mar 1;55(2):228-44. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt108. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24027300 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling carcinogenesis after radiotherapy using Poisson statistics: implications for IMRT, protons and ions.J Radiol Prot. 2009 Jun;29(2A):A143-57. doi: 10.1088/0952-4746/29/2A/S10. Epub 2009 May 19. J Radiol Prot. 2009. PMID: 19454805 Review.
-
Solar particle event storm shelter requirements for missions beyond low Earth orbit.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2018 May;17:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2018.02.002. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29753411 Review.
Cited by
-
Limitations in predicting the space radiation health risk for exploration astronauts.NPJ Microgravity. 2018 Apr 3;4:8. doi: 10.1038/s41526-018-0043-2. eCollection 2018. NPJ Microgravity. 2018. PMID: 29644336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Effects of Space Radiation and Development of Effective Countermeasures.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2014 Apr 1;1:10-43. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2014.02.004. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2014. PMID: 25258703 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing radiation selectively reduces skin regulatory T cells and alters immune function.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 24;9(6):e100800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100800. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24959865 Free PMC article.
-
Whole body proton irradiation causes acute damage to bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells in mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2017 Dec;93(12):1312-1320. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2017.1356941. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017. PMID: 28782442 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of changes over time in leukocyte counts in Yucatan minipigs irradiated with simulated solar particle event-like radiation.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2015 Jan;4:11-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2014.12.002. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25774341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostinelli S, Allison J, Amako K, Apostolakis J, Araujo H, Arce P, Asai M, Axen D, Banerjee S, Barrand G, Behner F, Bellagamba L, Boudreau J, Broglia L, Brunengo A, Burkhardt H, Chauvie S, Chuma J, Chytracek R, Cooperman G, Cosmo G, Degtyarenko P, Dell’Acqua A, Depaola G, Dietrich D, Enami R, Feliciello A, Ferguson C, Fesefeldt H, Folger G, Foppiano F, Forti A, Garelli S, Giani S, Giannitrapani R, Gibin D, GÛmez Cadenas JJ, Gonzlez I, Gracia Abril G, Greeniaus G, Greiner W, Grichine V, Grossheim A, Guatelli S, Gumplinger P, Hamatsu R, Hashimoto K, Hasui H, Heikkinen A, Howard A, Ivanchenko V, Johnson A, Jones FW, Kallenbach J, Kanaya N, Kawabata M, Kawabata Y, Kawaguti M, Kelner S, Kent P, Kimura A, Kodama T, Kokoulin R, Kossov M, Kurashige H, Lamanna E, LampÈn T, Lara V, Lefebure V, Lei F, Liendl M, Lockman W, Longo F, Magni S, Maire M, Medernach E, Minamimoto K, Mora de Freitas P, Morita Y, Murakami K, Nagamatu M, Nartallo R, Nieminen P, Nishimura T, Ohtsubo K, Okamura M, O’Neale S, Oohata Y, Paech K, Perl J, Pfeiffer A, Pia MG, Ranjard F, Rybin A, Sadilov S, Di Salvo E, Santin G, Sasaki T, Savvas N, Sawada Y, Scherer S, Sei S, Sirotenko V, Smith D, Starkov N, Stoecker H, Sulkimo J, Takahata M, Tanaka S, Tcherniaev E, Safai Tehrani E, Tropeano M, Truscott P, Uno H, Urban L, Urban P, Verderi M, Walkden A, Wander W, Weber H, Wellisch JP, Wenaus T, Williams DC, Wright D, Yamada T, Yoshida H, Zschiesche D. G4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl Inst Meth in Phys Res A. 2003;506:250–303.
-
- Amols HI, Lagueux B, Cagna D. Radiobiological effectiveness (RBE) of megavoltage X-ray and electron beams in radiotherapy. Radiat Res. 1986;105:58–67. - PubMed
-
- Coutrakon G, Benton E, Gridley D, Hickey T, Hubbard J, Koss P, Moyers M, Nelson G, Pecaut M, Sanders E, Shahnazi K. Simulation of a 36 h solar particle event at LLUMC using a proton beam scanning system. Nucl Inst Meth in Phys Res B. 2007;261:791–794.
-
- Hu S, Kim MH, McClellan GE, Cucinotta FA. Modeling the acute health effects of astronauts from exposure to large solar particle events. Health Phys. 2009;96:465–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

