Chemotherapy-induced structural changes in cerebral white matter and its correlation with impaired cognitive functioning in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 20725909
- PMCID: PMC6870393
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21033
Chemotherapy-induced structural changes in cerebral white matter and its correlation with impaired cognitive functioning in breast cancer patients
Abstract
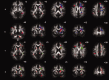
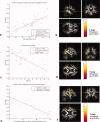
A subgroup of patients with breast cancer suffers from mild cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. To uncover the neural substrate of these mental complaints, we examined cerebral white matter (WM) integrity after chemotherapy using magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in combination with detailed cognitive assessment. Postchemotherapy breast cancer patients (n = 17) and matched healthy controls (n = 18) were recruited for DTI and neuropsychological testing, including the self-report cognitive failure questionnaire (CFQ). Differences in DTI WM integrity parameters [fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD)] between patients and healthy controls were assessed using a voxel-based two-sample-t-test. In comparison with healthy controls, the patient group demonstrated decreased FA in frontal and temporal WM tracts and increased MD in frontal WM. These differences were also confirmed when comparing this patient group with an additional control group of nonchemotherapy-treated breast cancer patients (n = 10). To address the heterogeneity observed in cognitive function after chemotherapy, we performed a voxel-based correlation analysis between FA values and individual neuropsychological test scores. Significant correlations of FA with neuropsychological tests covering the domain of attention and processing/psychomotor speed were found in temporal and parietal WM tracts. Furthermore, CFQ scores correlated negatively in frontal and parietal WM. These studies show that chemotherapy seems to affect WM integrity and that parameters derived from DTI have the required sensitivity to quantify neural changes related to chemotherapy-induced mild cognitive impairment.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham J, Haut MW, Moran MT, Filburn S, Lemiuex S, Kuwabara H ( 2008): Adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Effects on cerebral white matter seen in diffusion tensor imaging. Clin Breast Cancer 8: 88–91. - PubMed
-
- Ahles TA, Saykin AJ, Furstenberg CT, Cole B, Mott LA, Skalla K, Whedon MB, Bivens S, Mitchell T, Greenberg ER, Silberfarb PM ( 2002): Neuropsychologic impact of standard‐dose systemic chemotherapy in long‐term survivors of breast cancer and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 20: 485–493. - PubMed
-
- Army Individual Test Battery ( 1944): Manual of Directions and Scoring. Washington, DC: War Department, Adjutant General's Office.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

