Biomaterial topography alters healing in vivo and monocyte/macrophage activation in vitro
- PMID: 20725970
- PMCID: PMC4235956
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.32893
Biomaterial topography alters healing in vivo and monocyte/macrophage activation in vitro
Abstract
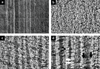
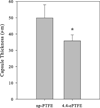
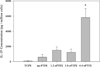
The effect of biomaterial topography on healing in vivo and monocyte/macrophage stimulation in vitro was assessed. A series of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) materials were characterized by increasing average intranodal distance of 1.2 μm (1.2-ePTFE), 3.0 μm (3.0-ePTFE), and 4.4 μm (4.4-ePTFE), but presented consistent surface chemistry with nonporous PTFE (np-PTFE). Subcutaneous implantation of 4.4-ePTFE into mice resulted in a statistically thinner capsule that appeared less organized and less dense than the np-PTFE response. In vitro, isolated monocytes/macrophages cultured on np-PTFE produced low levels of interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β), 1.2-ePTFE and 3.0-ePTFE stimulated intermediate levels, and 4.4-ePTFE stimulated a 15-fold increase over np-PTFE. Analysis of cDNA microarrays demonstrated that additional proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, including IL-1β, interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, monocyte chemotactic protein 1, and macrophage inflammatory protein 1-beta, were expressed at higher levels by monocytes/macrophages cultured on 4.4-ePTFE at 4 and 24 h, respectively. Expression ratios for several genes were quantified by RT-PCR and were consistent with those from the cDNA array results. These results demonstrate the effect of biomaterial topography on early proinflammatory cytokine production and gene transcription by monocytes/macrophages in vitro and decreased fibrous capsule thickness in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson JM. Biological responses to materials. Annu Rev Mater Res. 2001;31:81–110.
-
- Ziats NP, Miller KM, Anderson JM. In vitro and in vivo interactions of cells with biomaterials. Biomaterials. 1988;9(1):5–13. - PubMed
-
- Brodbeck WG, Voskerician G, Ziats NP, Nakayama Y, Matsuda T, Anderson JM. In vivo leukocyte cytokine mRNA responses to biomaterials are dependent on surface chemistry. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;64(2):320–329. - PubMed
-
- Bauer GJ, Arbabi S, Garcia IA, deHingh I, Rosengart MR, Maier RV. Adherence regulates macrophage signal transduction and primes tumor necrosis factor production. Shock. 2000;14(4):435–440. - PubMed
-
- Miller KM, Anderson JM. Human monocyte/macrophage activation and interleukin 1 generation by biomedical polymers. J Biomed Mater Res. 1988;22(8):713–731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

