Targeting of alpha-hemolysin by active or passive immunization decreases severity of USA300 skin infection in a mouse model
- PMID: 20726702
- PMCID: PMC2945289
- DOI: 10.1086/656043
Targeting of alpha-hemolysin by active or passive immunization decreases severity of USA300 skin infection in a mouse model
Abstract
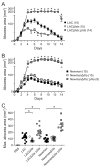
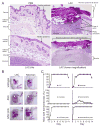
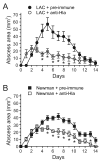
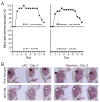
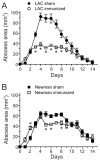
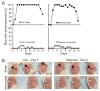
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) infections are predominantly those affecting skin and soft tissues. Although progress has been made, our knowledge of the molecules that contribute to the pathogenesis of CA-MRSA skin infections is incomplete. We tested the hypothesis that alpha-hemolysin (Hla) contributes to the severity of USA300 skin infections in mice and determined whether vaccination against Hla reduces disease severity. Isogenic hla-negative (Deltahla) strains caused skin lesions in a mouse infection model that were significantly smaller than those caused by wild-type USA300 and Newman strains. Moreover, infection due to wild-type strains produced dermonecrotic skin lesions, whereas there was little or no dermonecrosis in mice infected with Deltahla strains. Passive immunization with Hla-specific antisera or active immunization with a nontoxigenic form of Hla significantly reduced the size of skin lesions caused by USA300 and prevented dermonecrosis. We conclude that Hla is a potential target for therapeutics or vaccines designed to moderate severe S. aureus skin infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Expectations regarding vaccines and immune therapies directed against Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 1;203(11):1692-3; author reply 1693-4. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir141. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21593000 No abstract available.
References
-
- Voyich JM, Otto M, Mathema B, et al. Is Panton-Valentine leukocidin the major virulence determinant in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease? J Infect Dis. 2006;194:1761–70. - PubMed
-
- Ezepchuk YV, Leung DY, Middleton MH, Bina P, Reiser R, Norris DA. Staphylococcal toxins and protein A differentially induce cytotoxicity and release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;107:603–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

