Effects of proton radiation dose, dose rate and dose fractionation on hematopoietic cells in mice
- PMID: 20726731
- PMCID: PMC3405897
- DOI: 10.1667/RR1979.1
Effects of proton radiation dose, dose rate and dose fractionation on hematopoietic cells in mice
Abstract
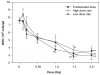
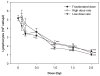
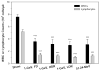
The present study evaluated the acute effects of radiation dose, dose rate and fractionation as well as the energy of protons in hematopoietic cells of irradiated mice. The mice were irradiated with a single dose of 51.24 MeV protons at a dose of 2 Gy and a dose rate of 0.05-0.07 Gy/min or 1 GeV protons at doses of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 1.5 and 2 Gy delivered in a single dose at dose rates of 0.05 or 0.5 Gy/min or in five daily dose fractions at a dose rate of 0.05 Gy/min. Sham-irradiated animals were used as controls. The results demonstrate a dose-dependent loss of white blood cells (WBCs) and lymphocytes by up to 61% and 72%, respectively, in mice irradiated with protons at doses up to 2 Gy. The results also demonstrate that the dose rate, fractionation pattern and energy of the proton radiation did not have significant effects on WBC and lymphocyte counts in the irradiated animals. These results suggest that the acute effects of proton radiation on WBC and lymphocyte counts are determined mainly by the radiation dose, with very little contribution from the dose rate (over the range of dose rates evaluated), fractionation and energy of the protons.
Figures
References
-
- Hellweg CE, Baumstark-Khan C. Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts’ risk from space radiation. Naturwissenschaften. 2007;94:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JW, Cucinotta FA, Shinn JL, Simonsen LC, Dubey RR, Jordan WR, Jones TD, Chang CK, Kim MY. Shielding from solar particle event exposures in deep space. Radiat Res. 1999;30:361–382. - PubMed
-
- Smart DF, Shea MA. The local time dependence of the anisotropic solar cosmic ray flux. Adv Space Res. 2003;32:109–114. - PubMed
-
- Koenig KL, Goans RE, Hatchett RJ, Mettler FA, Jr, Schumacher TA, Noji EK, Jarrett DG. Medical treatment of radiological casualties: current concepts. Ann Emerg Med. 2005;45:643–652. - PubMed
-
- Coleman CN, Blakely WF, Fike JR, MacVittie TJ, Metting NF, Mitchell JB, Moulder JE, Preston RJ, Seed TM, Wong RS. Radiat Res; Molecular and cellular biology of moderate-dose (1–10 Gy) radiation and potential mechanisms of radiation protection: report of a workshop; Bethesda, Maryland. December 17–18, 2001; 2003. pp. 812–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

