Amphiregulin regulates the activation of ERK and Akt through epidermal growth factor receptor and HER3 signals involved in the progression of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 20726858
- PMCID: PMC11158290
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01671.x
Amphiregulin regulates the activation of ERK and Akt through epidermal growth factor receptor and HER3 signals involved in the progression of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
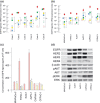
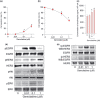
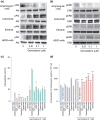
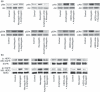
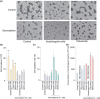
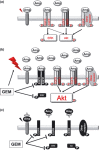
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignancies. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), HER3, Akt, and amphiregulin have been recognized as targets for pancreatic cancer therapy. Although gemcitabine + erlotinib has been the recommended chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer, the prognosis is extremely poor. The development of molecularly targeted therapies has been required for patients with pancreatic cancer. To assess the validation of amphiregulin as a target for pancreatic cancer therapy, we examined its expression in pancreatic cancer using real-time PCR analyses and ELISA. We also measured the apoptotic cell rate using TUNEL assays. In addition, alterations in signaling pathways were detected by immunoblotting analyses. Treatment with gemcitabine, which reduced the cell viability and augmented the cell apoptotic rate, activated and subsequently attenuated ERK and EGFR signals. However, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, or cisplatin treatment enhanced the Akt activation, heterodimer formation of EGFR with HER3, and secretion of amphiregulin, indicating that the presence of gemcitabine promoted the activity of targeted molecules including amphiregulin, Akt, and HER3 for pancreatic cancer therapy. Combined treatment with an inhibitor for amphiregulin and gemcitabine, paclitaxel, or cisplatin induced synergistic antitumor effects, accompanied by the suppression of Akt and ERK activation. Blockade of amphiregulin suppressed the activities of EGFR, HER3, and Akt and the expression of amphiregulin itself. According to this evidence, combination chemotherapy of conventional anticancer drugs plus an inhibitor for amphiregulin would allow us to provide more favorable clinical outcomes for patients with pancreatic cancer.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling mediates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors toward PTH-stimulated osteoblasts and osteocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050099. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300521 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 increases response to gemcitabine and delays progression of pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer. 2013 Sep 11;12(1):104. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-104. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24025152 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of the effect of erlotinib by genistein in pancreatic cancer: the role of Akt and nuclear factor-kappaB.Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 1;66(21):10553-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2333. Cancer Res. 2006. Retraction in: Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 15;78(18):5472. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1168. PMID: 17079479 Retracted.
-
Overcoming resistance to molecularly targeted anticancer therapies: Rational drug combinations based on EGFR and MAPK inhibition for solid tumours and haematologic malignancies.Drug Resist Updat. 2007 Jun;10(3):81-100. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2007.03.003. Epub 2007 May 7. Drug Resist Updat. 2007. PMID: 17482503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic cancer: molecular pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Jul;6(7):412-22. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.89. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19506583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of NRF2 by PIK-75 augments sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine.Int J Oncol. 2014 Mar;44(3):959-69. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2229. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24366069 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiregulin activates regulatory T lymphocytes and suppresses CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor response in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):32138-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5171. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26451607 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodality Approaches to Treat Hypoxic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Microenvironment.Genes Cancer. 2012 Feb;3(2):141-51. doi: 10.1177/1947601912457025. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23050046 Free PMC article.
-
Tricellular tight junction protein LSR/angulin-1 contributes to the epithelial barrier and malignancy in human pancreatic cancer cell line.Histochem Cell Biol. 2020 Jan;153(1):5-16. doi: 10.1007/s00418-019-01821-4. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Histochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31650247
-
Amphiregulin Regulates Phagocytosis-Induced Cell Death in Monocytes via EGFR and the Bcl-2 Protein Family.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Nov 3;2019:1603131. doi: 10.1155/2019/1603131. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 32082070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 2009; 59: 225–49. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004; 363: 1049–57. - PubMed
-
- Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen MJ et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first‐line therapy for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 2403–13. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J et al. Erlotinib+gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada clinical trials group. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1960–6. - PubMed
-
- Welch SA, Moore MJ. Combination chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer: time to raise the white flag? J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2159–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

