Reactive oxygen species are involved in regulating alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated vascular smooth muscle contraction
- PMID: 20727219
- PMCID: PMC2931462
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-67
Reactive oxygen species are involved in regulating alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated vascular smooth muscle contraction
Abstract
Background: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were shown to mediate aberrant contractility in hypertension, yet the physiological roles of ROS in vascular smooth muscle contraction have remained elusive. This study aimed to examine whether ROS regulate alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated contraction by altering myosin phosphatase activities.
Methods: Using endothelium-denuded rat tail artery (RTA) strips, effects of anti-oxidants on isometric force, ROS production, phosphorylation of the 20-kDa myosin light chain (MLC20), and myosin phosphatase stimulated by alpha1-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine were examined.
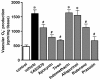
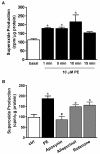
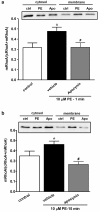
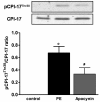
Results: An antioxidant, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), and two NADPH oxidase inhibitors, apocynin and VAS2870, dose-dependently inhibited contraction activated by phenylephrine. Phenylephrine stimulated superoxide anion production that was diminished by the pretreatment of apocynin, VAS2870, superoxide scavenger tiron or mitochondria inhibitor rotenone, but not by xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol or cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin. Concurrently, NADPH oxidase activity in RTA homogenates increased within 1 min upon phenylephrine stimulation, sustained for 10 min, and was abolished by the co-treatment with apocynin, but not allopurinol or rotenone. Phenylephrine-induced MLC20 phosphorylation was dose-dependently decreased by apocynin. Furthermore, apocynin inhibited phenylephrine-stimulated RhoA translocation to plasma membrane and phosphorylation of both myosin phosphatase regulatory subunit MYPT1Thr855 and myosin phosphatase inhibitor CPI-17Thr38.
Conclusions: ROS, probably derived from NADPH oxidase and mitochondria, partially regulate alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated smooth muscle contraction by altering myosin phosphatase-mediated MLC20 phosphorylation through both RhoA/Rho kinase- and CPI-17-dependent pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Y27632, a Rho-activated kinase inhibitor, normalizes dysregulation in alpha1-adrenergic receptor-induced contraction of Lyon hypertensive rat artery smooth muscle.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;23(2):169-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00658.x. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19298234 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-dependent activation of RhoA/Rho-kinase in pulmonary artery: Role of Src-family kinases and ARHGEF1.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Sep;110:316-331. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jul 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28673614 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 in contraction of vascular smooth muscle.Life Sci. 2005 Jan 7;76(8):877-88. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.10.010. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15589965
-
Signaling for contraction and relaxation in smooth muscle of the gut.Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:345-74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.68.040504.094707. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16460276 Review.
-
Role of serine-threonine phosphoprotein phosphatases in smooth muscle contractility.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Mar;304(6):C485-504. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00161.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23325405 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethers and esters derived from apocynin avoid the interaction between p47phox and p22phox subunits of NADPH oxidase: evaluation in vitro and in silico.Biosci Rep. 2013 Aug 2;33(4):e00055. doi: 10.1042/BSR20130029. Biosci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23802190 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress, Reductive Stress and Antioxidants in Vascular Pathogenesis and Aging.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 19;12(5):1126. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051126. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOX1, 2, 4, 5: counting out oxidative stress.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;164(3):866-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01249.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21323893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lidocaine relaxation in isolated rat aortic rings is enhanced by endothelial removal: possible role of Kv, KATP channels and A2a receptor crosstalk.BMC Anesthesiol. 2016 Dec 3;16(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12871-016-0286-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 27914476 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced vascular neuronal nitric-oxide synthase-derived nitric-oxide production underlies the pressor response caused by peripheral N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation in conscious rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Aug;342(2):461-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.194464. Epub 2012 May 11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22580349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irani K. Oxidant signaling in vascular cell growth, death, and survival: a review of the roles of reactive oxygen species in smooth muscle and endothelial cell mitogenic and apoptotic signaling. Circ Res. 2000;87:179–183. - PubMed
-
- Laursen JB, Rajagopalan S, Galis Z, Tarpey M, Freeman BA, Harrison DG. Role of superoxide in angiotensin II-induced but not catecholamine-induced hypertension. Circulation. 1997;95:588–93. - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan S, Kurz S, Munzel T, Tarpey M, Freeman BA, Griendling KK, Harrison DG. Angiotensin II-mediated hypertension in the rat increases vascular superoxide production via membrane NADH/NADPH oxidase activation. Contribution to alterations of vasomotor tone. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:1916–1923. doi: 10.1172/JCI118623. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sedeek MH, Llinas MT, Drummond H, Fortepiani L, Abram SR, Alexander BT, Reckelhoff JF, Granger JP. Role of reactive oxygen species in endothelin-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;42:806–810. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000084372.91932.BA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

