Anxiolytic-like effects of 8-acetylene imidazobenzodiazepines in a rhesus monkey conflict procedure
- PMID: 20727364
- PMCID: PMC2963662
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.08.011
Anxiolytic-like effects of 8-acetylene imidazobenzodiazepines in a rhesus monkey conflict procedure
Abstract
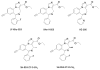
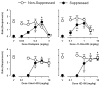
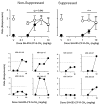
Conflict procedures can be used to study the receptor mechanisms underlying the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines and other GABA(A) receptor modulators. In the present study, we first determined the efficacy and binding affinity of the benzodiazepine diazepam and recently synthesized GABA(A) receptor modulators JY-XHe-053, XHe-II-053, HZ-166, SH-053-2'F-S-CH₃ and SH-053-2'F-R-CH₃ at GABA(A) receptors containing α1, α2, α3 and α5 subunits. Results from these studies suggest that each compound displayed lower efficacy at GABA(A) receptors containing α1 subunits and varying degrees of efficacy and affinity at GABA(A) receptors containing α2, α3 and α5 subunits. Next, we assessed their anxiolytic effects using a rhesus monkey conflict procedure in which behavior was maintained under a fixed-ratio schedule of food delivery in the absence (non-suppressed responding) and presence (suppressed responding) of response-contingent electric shock. Relatively non-selective compounds, such as diazepam and JY-XHe-053 produced characteristic increases in rates of suppressed responding at low to intermediate doses and decreased the average rates of non-suppressed responding at higher doses. XHe-II-053 and HZ-166 also produced increases in suppressed responding at low to intermediate doses, but were ineffective at decreasing rates of non-suppressed responding, consistent with their relatively low efficacy at GABA(A) receptors containing α1 and α5 subunits. In contrast, SH-053-2'F-S-CH₃ and SH-053-2'F-R-CH₃ produced only partial increases in suppressed responding and were ineffective on non-suppressed responding, consistent with their profiles as partial agonists at GABA(A) receptors containing α2, α3 and α5 subunits. These behavioral effects suggest that the anxiolytic and rate-reducing effects of GABA(A) receptor positive modulators are dependent on their relative efficacy and affinity at different GABA(A) receptor subtypes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors: do subtle differences in activity at alpha1 plus alpha5 versus alpha2 plus alpha3 subunits account for dissimilarities in behavioral effects in rats?Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar 17;34(2):376-86. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20074611 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-conflict effects of benzodiazepines in rhesus monkeys: relationship with therapeutic doses in humans and role of GABAA receptors.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Jan;184(2):201-11. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0228-8. Epub 2005 Dec 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16378217
-
Abuse-related effects of subtype-selective GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators in an assay of intracranial self-stimulation in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Jul;234(14):2091-2101. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4615-8. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28365836 Free PMC article.
-
GABAA receptor subtype-selective modulators. II. α5-selective inverse agonists for cognition enhancement.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1203-14. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371314. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050171 Review.
-
GABAA receptor subtype-selective modulators. I. α2/α3-selective agonists as non-sedating anxiolytics.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1176-202. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371350. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050172 Review.
Cited by
-
Different Benzodiazepines Bind with Distinct Binding Modes to GABAA Receptors.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Aug 17;13(8):2033-2039. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00144. Epub 2018 Jul 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29767950 Free PMC article.
-
8-Substituted Triazolobenzodiazepines: In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacology in Relation to Structural Docking at the α1 Subunit-Containing GABAA Receptor.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:625233. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.625233. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33959005 Free PMC article.
-
Search for α3β₂/₃γ2 subtype selective ligands that are stable on human liver microsomes.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Jan 1;21(1):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.10.057. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23218469 Free PMC article.
-
The role of α5 GABAA receptor agonists in the treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(31):5069-76. doi: 10.2174/1381612819666131216114612. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24345268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sh-I-048A, an in vitro non-selective super-agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors: the approximated activation of receptor subtypes may explain behavioral effects.Brain Res. 2014 Mar 20;1554:36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.01.036. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24472579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atack JR, Wafford KA, Tye SJ, Cook SM, Sohal B, Pike A, Sur C, Melillo D, Bristow L, Bromidge F, Ragan I, Kerby J, Street L, Carling R, Castro JL, Whiting P, Dawson GR, McKernan RM. TPA023 [7-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-6-(2-ethyl-2H-1,2,4-triazol-30ylmethoxy)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine], an agonist selective for α2 and α3-containing GABAA receptors, is a nonsedating anxiolytic in rodents and primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:410–422. - PubMed
-
- Collinson N, Kuenzi FM, Jarolimek W, Maubach KA, Cothliff R, Sur C, Smith A, Otu FM, Howell O, Atack JR, McKernan RM, Seabrook GR, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ, Rosahl TW. Enhanced learning and memory and altered GABAergic synaptic transmission in mice lacking the alpha 5 subunit of the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci. 2002;22:5572–5580. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cook L, Davidson AB. Effects of behaviorally active drugs in a conflict-punishment procedure in rats. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LO, editors. The benzodiazepines. Raven; New York: 1973. pp. 327–345.
-
- Cook JM, Zhou H, Huang S, Srirama Sarma PVV, Zhang C. Stereospecific anxiolytic and anticonvulsant agents with reduced muscle-relaxant, sedative-hypnotic and ataxic effects. US Patent. 7,618,958 B2. 2009. Issued November 17,2009.
-
- Cook JM, Edwankar R, Edwankar C, Huang S, Jain H, Rivas F, Yang J, Zhou H. Selective anticonvulsant agents and their uses. 2010. T08025US Utility, Serial # 12/725,763, Filed March 17, 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

