Interparental relationship dynamics and cardiac vagal functioning in infancy
- PMID: 20727595
- PMCID: PMC2997926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2010.07.005
Interparental relationship dynamics and cardiac vagal functioning in infancy
Abstract
This study examined associations between interparental relationship dynamics and vagus system functioning in infancy. The functioning of the vagus system, part of the parasympathetic nervous system, indexes emotional reactivity and regulation. Interparental avoidance and dyadic adjustment constitute the focus of this study in order to bring attention to relationship dynamics not subsumed under overt conflict. Infants' baseline vagal tone and change in vagal tone in response to a novel toy were assessed at 5 months in a sample of high-risk mother-infant dyads (n=77). Maternal report of interparental avoidance demonstrated an association with infants' baseline vagal tone, while interparental dyadic adjustment was associated with change in infants' vagal tone from baseline to the novel toy. Infant gender moderated these associations. Maternal sensitivity did not mediate interparental relationship dynamics and infants' vagal functioning. Results are discussed in the context of emotional security theory.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
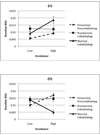
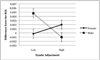
References
-
- Ablow JC. When Parents Conflict or Disengage: Children's Perceptions of Parents' Marital Distress Predict School Adaptation. In: Cowan Philip A, Cowan Carolyn Pape, Ablow Jennifer C, Johnson Vanessa Kahen, Measelle Jeffrey R., editors. The family context of parenting in children's adaptation to elementary school. Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 2005. pp. 189–208.
-
- Avison WR, Turner RJ, Noh S. Screening for problem parenting: Preliminary evidence on a promising instrument. Child Abuse & Neglect. 1986;10:157–170. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates; 1988.
-
- Balaban MT. Affective influences on startle in five-month-old infants: Reactions to facial expressions of emotion. Child Development. 1995;66:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Haim Y, Marshall PJ, Fox NA. Developmental changes in heart period and high-frequency heart period variability from 4 months to 4 years of age. Developmental Psychobiology. 2000;37:44–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

