Modulation of BMP signaling by Noggin is required for the maintenance of palatal epithelial integrity during palatogenesis
- PMID: 20727875
- PMCID: PMC3010875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.08.014
Modulation of BMP signaling by Noggin is required for the maintenance of palatal epithelial integrity during palatogenesis
Abstract
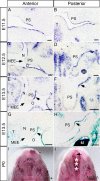
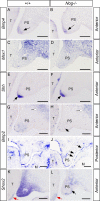
BMP signaling plays many important roles during organ development, including palatogenesis. Loss of BMP signaling leads to cleft palate formation. During development, BMP activities are finely tuned by a number of modulators at the extracellular and intracellular levels. Among the extracellular BMP antagonists is Noggin, which preferentialy binds to BMP2, BMP4 and BMP7, all of which are expressed in the developing palatal shelves. Here we use targeted Noggin mutant mice as a model for gain of BMP signaling function to investigate the role of BMP signaling in palate development. We find prominent Noggin expression in the palatal epithelium along the anterior-posterior axis during early palate development. Loss of Noggin function leads to overactive BMP signaling, particularly in the palatal epithelium. This results in disregulation of cell proliferation, excessive cell death, and changes in gene expression, leading to formation of complete palatal cleft. The excessive cell death in the epithelium disrupts the palatal epithelium integrity, which in turn leads to an abnormal palate-mandible fusion and prevents palatal shelf elevation. This phenotype is recapitulated by ectopic expression of a constitutively active form of BMPR-IA but not BMPR-IB in the epithelium of the developing palate; this suggests a role for BMPR-IA in mediating overactive BMP signaling in the absence of Noggin. Together with the evidence that overexpression of Noggin in the palatal epithelium does not cause a cleft palate defect, we conclude from our results that Noggin mediated modulation of BMP signaling is essential for palatal epithelium integrity and for normal palate development.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Altered BMP-Smad4 signaling causes complete cleft palate by disturbing osteogenesis in palatal mesenchyme.J Mol Histol. 2021 Feb;52(1):45-61. doi: 10.1007/s10735-020-09922-4. Epub 2020 Nov 7. J Mol Histol. 2021. PMID: 33159638
-
Rescue of cleft palate in Msx1-deficient mice by transgenic Bmp4 reveals a network of BMP and Shh signaling in the regulation of mammalian palatogenesis.Development. 2002 Sep;129(17):4135-46. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.17.4135. Development. 2002. PMID: 12163415
-
Constitutively active mutation of ACVR1 in oral epithelium causes submucous cleft palate in mice.Dev Biol. 2016 Jul 15;415(2):306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.06.014. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26116174 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Palatogenesis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;115:59-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.002. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26589921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional regulation of palatal growth and patterning along the anterior-posterior axis in mice.J Anat. 2005 Nov;207(5):655-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00474.x. J Anat. 2005. PMID: 16313398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noggin is required for early development of murine upper incisors.J Dent Res. 2012 Apr;91(4):394-400. doi: 10.1177/0022034511435939. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Dent Res. 2012. PMID: 22302143 Free PMC article.
-
Bmp signaling regulates a dose-dependent transcriptional program to control facial skeletal development.Development. 2012 Feb;139(4):709-19. doi: 10.1242/dev.073197. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Development. 2012. PMID: 22219353 Free PMC article.
-
Murine craniofacial development requires Hdac3-mediated repression of Msx gene expression.Dev Biol. 2013 May 15;377(2):333-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23506836 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent palate morphology in turtles and birds correlates with differences in proliferation and BMP2 expression during embryonic development.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2014 Feb;322(2):73-85. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22547. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2014. PMID: 24323766 Free PMC article.
-
The short stature homeobox 2 (Shox2)-bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway regulates dorsal mesenchymal protrusion development and its temporary function as a pacemaker during cardiogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 23;290(4):2007-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619007. Epub 2014 Dec 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25488669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alappat SR, Zhang Z, Suzuki K, Zhang X, Liu H, Jiang R, Yamada G, Chen YP. The cellular and molecular etiology of the cleft secondary palate in Fgf10 mutant mice. Dev. Biol. 2005;277:102–113. - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, Lyons KM, Mishina Y, Seykora JT, Crenshaw EB, 3rd., Millar SE. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development. 2004;131:2257–2268. - PubMed
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Kemp C, Belo JA, Anderson RM, May SR, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Harland RM, Rossant J, De Robertis EM. The organizer factors Chordin and Noggin are required for mouse forebrain development. Nature. 2000;403:658–661. - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Van Hul W. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev. Biol. 2002;250:231–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

