The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in trace fear conditioning
- PMID: 20727979
- PMCID: PMC2949463
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.08.001
The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in trace fear conditioning
Abstract
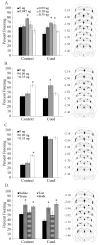
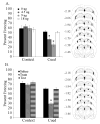
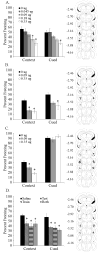
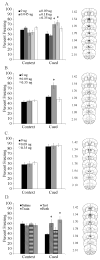
Acute nicotine enhances multiple types of learning including trace fear conditioning but the underlying neural substrates of these effects are not well understood. Trace fear conditioning critically involves the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, which both express nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). Therefore, nicotine could act in either or both areas to enhance trace fear conditioning. To identify the underlying neural areas and nAChR subtypes, we examined the effects of infusion of nicotine, or nicotinic antagonists dihydro-beta-erythroidine (DHβE: high-affinity nAChRs) or methyllycaconitine (MLA: low-affinity nAChRs) into the dorsal hippocampus, ventral hippocampus, and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) on trace and contextual fear conditioning. We found that the effects of nicotine on trace and contextual fear conditioning vary by brain region and nAChR subtype. The dorsal hippocampus was involved in the effects of nicotine on both trace and contextual fear conditioning but each task was sensitive to different doses of nicotine. Additionally, dorsal hippocampal infusion of the antagonist DHβE produced deficits in trace but not contextual fear conditioning. Nicotine infusion into the ventral hippocampus produced deficits in both trace and contextual fear conditioning. In the mPFC, nicotine enhanced trace but not contextual fear conditioning. Interestingly, infusion of the antagonists MLA or DHβE in the mPFC also enhanced trace fear conditioning. These findings suggest that nicotine acts on different substrates to enhance trace versus contextual fear conditioning, and that nicotine-induced desensitization of nAChRs in the mPFC may contribute to the effects of nicotine on trace fear conditioning.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippocampal alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor involvement in the enhancing effect of acute nicotine on contextual fear conditioning.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 3;27(40):10870-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3242-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17913920 Free PMC article.
-
The hippocampus and cingulate cortex differentially mediate the effects of nicotine on learning versus on ethanol-induced learning deficits through different effects at nicotinic receptors.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 Aug;34(9):2167-79. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.45. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19404242 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine ameliorates NMDA receptor antagonist-induced deficits in contextual fear conditioning through high-affinity nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the hippocampus.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Mar;60(4):617-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.004. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21167848 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning and synaptic plasticity by nicotine.Mol Neurobiol. 2008 Aug;38(1):101-21. doi: 10.1007/s12035-008-8037-9. Epub 2008 Aug 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18690555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prefrontal neuronal circuits of contextual fear conditioning.Genes Brain Behav. 2015 Jan;14(1):22-36. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12181. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Genes Brain Behav. 2015. PMID: 25287656 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent transitions in reflexive and non-reflexive behavior: Review of fear conditioning and impulse control in rodent models.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Nov;70:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.06.026. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27339692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Sep;133:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27264248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic regulation of local and long-range input balance drives top-down attentional circuit maturation.Sci Adv. 2021 Mar 5;7(10):eabe1527. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe1527. Print 2021 Mar. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33674307 Free PMC article.
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate modulates acquisition and extinction of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 May;106:109-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013. PMID: 23454534 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic fluoxetine ameliorates adolescent chronic nicotine exposure-induced long-term adult deficits in trace conditioning.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:272-283. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.033. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28778833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman DM, Grubb M, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Feldon J, Rawlins JNP. Ventral hippocampal lesions affect anxiety but not spatial learning. Behavioural Brain Research. 2003;139:197–213. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats. Different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol. Experimental Brain Research. Experimentelle Hirnforschung. Experimentation Cerebrale. 2001;139:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Crouching as an index of fear. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology. 1969;67:370–5. - PubMed
-
- Blum S, Hebert AE, Dash PK. A role for the prefrontal cortex in recall of recent and remote memories. Neuroreport. 2006;17:341–4. - PubMed
-
- Brega AG, Grigsby J, Kooken R, Hamman RF, Baxter J. The impact of executive cognitive functioning on rates of smoking cessation in the San Luis Valley Health and Aging Study. Age and Ageing. 2008;37:521–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

