Potentiation of polarized intestinal Caco-2 cell responsiveness to probiotics complexed with secretory IgA
- PMID: 20729211
- PMCID: PMC2962490
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.135111
Potentiation of polarized intestinal Caco-2 cell responsiveness to probiotics complexed with secretory IgA
Abstract
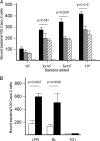
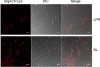
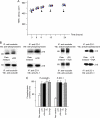
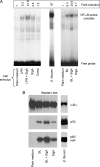
The precise mechanisms underlying the interaction between intestinal bacteria and the host epithelium lead to multiple consequences that remain poorly understood at the molecular level. Deciphering such events can provide valuable information as to the mode of action of commensal and probiotic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal environment. Potential roles of such microorganisms along the privileged target represented by the mucosal immune system include maturation prior, during and after weaning, and the reduction of inflammatory reactions in pathogenic conditions. Using human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell grown as polarized monolayers, we found that association of a Lactobacillus or a Bifidobacterium with nonspecific secretory IgA (SIgA) enhanced probiotic adhesion by a factor of 3.4-fold or more. Bacteria alone or in complex with SIgA reinforced transepithelial electrical resistance, a phenomenon coupled with increased phosphorylation of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1 and occludin. In contrast, association with SIgA resulted in both enhanced level of nuclear translocation of NF-κB and production of epithelial polymeric Ig receptor as compared with bacteria alone. Moreover, thymic stromal lymphopoietin production was increased upon exposure to bacteria and further enhanced with SIgA-based complexes, whereas the level of pro-inflammatory epithelial cell mediators remained unaffected. Interestingly, SIgA-mediated potentiation of the Caco-2 cell responsiveness to the two probiotics tested involved Fab-independent interaction with the bacteria. These findings add to the multiple functions of SIgA and underscore a novel role of the antibody in interaction with intestinal bacteria.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of secretory IgA in the mucosal sensing of commensal bacteria.Gut Microbes. 2014;5(6):688-95. doi: 10.4161/19490976.2014.983763. Gut Microbes. 2014. PMID: 25536286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by unconjugated bilirubin.Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104(3):390-401. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510000474. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20412608
-
Secretions of Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus Protect Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Mar;64(3):404-412. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001310. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28230606
-
Lactobacillus plantarum MB452 enhances the function of the intestinal barrier by increasing the expression levels of genes involved in tight junction formation.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Dec 9;10:316. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-316. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21143932 Free PMC article.
-
N-Glycans on secretory component: mediators of the interaction between secretory IgA and gram-positive commensals sustaining intestinal homeostasis.Gut Microbes. 2011 Sep 1;2(5):287-93. doi: 10.4161/gmic.2.5.18269. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Gut Microbes. 2011. PMID: 22067937 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of orally fed a select mixture of Bacillus probiotics on intestinal T-cell migration in weaned MUC4 resistant pigs following Escherichia coli challenge.Vet Res. 2016 Jul 16;47(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0355-8. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27424033 Free PMC article.
-
Current understanding of the gut microbiota shaping mechanisms.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Aug 21;26(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0554-5. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 31434568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Selected Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain Promotes EGFR-Independent Akt Activation in an Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-Infected IPEC-J2 Cell Model.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 27;10(4):e0125717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125717. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25915861 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinaceous Molecules Mediating Bifidobacterium-Host Interactions.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 3;7:1193. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01193. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27536282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of secretory immunoglobulin A in the natural sensing of commensal bacteria by mouse Peyer's patch dendritic cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 16;287(47):40074-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.405001. Epub 2012 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23027876 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

