Clusterin synergizes with IL-2 for the expansion and IFN-γ production of natural killer cells
- PMID: 20729304
- PMCID: PMC6608014
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0310157
Clusterin synergizes with IL-2 for the expansion and IFN-γ production of natural killer cells
Abstract
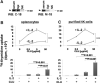
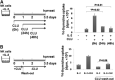
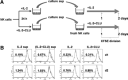
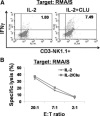
CLU is a secreted, multifunctional protein implicated in several immunologic and pathologic conditions. As the level of serum CLU was shown to be elevated during inflammatory responses, we questioned if CLU might interact with circulating lymphocytes leading to functional consequences. To assess this possibility directly, mouse splenocytes and purified NK cells were cultured with varying dose of CLU, and its effect on cell proliferation was examined. Our data showed that CLU up-regulated DNA synthesis and expansion of NK cells significantly in response to a suboptimal, but not maximal, dose of IL-2, and CLU alone did not exhibit such effects. This CLU-mediated synergy required the co-presence of CLU at the onset of IL-2 stimulation and needed a continuous presence during the rest of the culture. Importantly, NK cells stimulated with CLU showed increased formation of cell clusters and a CD69 activation receptor, representing a higher cellular activation status compared with those from the control group. Furthermore, these NK cells displayed elevated IFN-γ production upon RMA/S tumor target exposures, implying that CLU regulates not only NK cell expansion but also effector function of NK cells. Collectively, our data present a previously unrecognized function of CLU as a novel regulator of NK cells via providing costimulation required for cell proliferation and IFN-γ secretion. Therefore, the role of CLU on NK cells should be taken into consideration for the previously observed, diverse functions of CLU in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic proliferation and activation of natural killer cells by interleukin 12 and interleukin 18.Cytokine. 1999 Nov;11(11):822-30. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1999.0501. Cytokine. 1999. PMID: 10547269
-
Stem cell factor enhances interleukin-2-mediated expansion of murine natural killer cells in vivo.Blood. 1997 Nov 1;90(9):3647-53. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9345049
-
Interleukin 2-induced proliferation of murine natural killer cells in vivo.J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):173-88. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.173. J Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 1688606 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha are costimulators of interferon gamma production by natural killer cells in severe combined immunodeficiency mice with listeriosis, and interleukin 10 is a physiologic antagonist.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3725-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3725. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8097322 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-induced suppression of interferon-gamma production and enhancement of interleukin-10 production by natural killer (NK) cells: paralleled to CD4+ T cells.Mol Immunol. 2005 May;42(9):1023-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.09.035. Epub 2004 Nov 23. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15829292
Cited by
-
Astrocytic response mediated by the CLU risk allele inhibits OPC proliferation and myelination in a human iPSC model.Cell Rep. 2023 Aug 29;42(8):112841. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112841. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37494190 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating host secreted protein gene expression: an indirect approach by HPV11/16 E6/E7 to suppress PBMC cytokine secretion.Virol J. 2024 Aug 2;21(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02432-9. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39095779 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils Lose the Capacity to Suppress T Cell Proliferation Upon Migration Towards Inflamed Joints in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:795260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.795260. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095871 Free PMC article.
-
An IL-15 Superagonist, ALT-803, Enhances Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Elicited by the Monoclonal Antibody NEO-201 Against Human Carcinoma Cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019 Apr;34(3):147-159. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2018.2628. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019. PMID: 30601063 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant memantine and Lactobacillus plantarum treatment attenuates cognitive impairments in APP/PS1 mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):628-649. doi: 10.18632/aging.102645. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 31907339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trougakos, I. P., Gonos, E. S. (2006) Regulation of clusterin/apolipoprotein J, a functional homologue to the small heat shock proteins, by oxidative stress in aging and age‐related diseases. Free Radic. Res. 40, 1324–1334. - PubMed
-
- Blaschuk, O., Burdzy, K., Fritz, I. B. (1983) Purification and characterization of a cell‐aggregating factor (clusterin), the major glycoprotein in ram rete testis fluid. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 7714–7720. - PubMed
-
- Shannan, B., Seifert, M., Leskov, K., Willis, J., Boothman, D., Tilgen, W., Reichrath, J. (2006) Challenge and promise: roles for clusterin in pathogenesis, progression and therapy of cancer. Cell Death Differ. 13, 12–19. - PubMed
-
- Falgarone, G., Chiocchia, G. (2009) Chapter 8: clusterin: a multifacet protein at the crossroad of inflammation and autoimmunity. Adv. Cancer Reis. 104, 139–170. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin, L., Zhu, G., Mistry, M., Ley‐Ebert, C., Stuart, W. D., Florio, C. J., Groen, P. A., Witt, S. A., Kimball, T. R., Witte, D. P., Harmony, J. A., Aronow, B. J. (2000) Apolipoprotein J/clusterin limits the severity of murine autoimmune myocarditis. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 1105–1113. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

