Roles of multiple acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductases in polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16
- PMID: 20729355
- PMCID: PMC2950492
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00207-10
Roles of multiple acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductases in polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16
Abstract
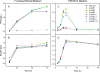
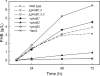
The bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16 synthesizes polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) from acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) through reactions catalyzed by a β-ketothiolase (PhaA), an acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (PhaB), and a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase (PhaC). An operon of three genes encoding these enzymatic steps was discovered in R. eutropha and has been well studied. Sequencing and analysis of the R. eutropha genome revealed putative isologs for each of the PHB biosynthetic genes, many of which had never been characterized. In addition to the previously identified phaB1 gene, the genome contains the isologs phaB2 and phaB3 as well as 15 other potential acetoacetyl-CoA reductases. We have investigated the roles of the three phaB isologs by deleting them from the genome individually and in combination. It was discovered that the gene products of both phaB1 and phaB3 contribute to PHB biosynthesis in fructose minimal medium but that in plant oil minimal medium and rich medium, phaB3 seems to be unexpressed. This raises interesting questions concerning the regulation of phaB3 expression. Deletion of the gene phaB2 did not result in an observable phenotype under the conditions tested, although this gene does encode an active reductase. Addition of the individual reductase genes to the genome of the ΔphaB1 ΔphaB2 ΔphaB3 strain restored PHB production, and in the course of our complementation experiments, we serendipitously created a PHB-hyperproducing mutant. Measurement of the PhaB and PhaA activities of the mutant strains indicated that the thiolase reaction is the limiting step in PHB biosynthesis in R. eutropha H16 during nitrogen-limited growth on fructose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of multiple beta-ketothiolase deletion mutations in Ralstonia eutropha H16 on the composition of 3-mercaptopropionic acid-containing copolymers.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Aug;76(16):5373-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01058-10. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20601511 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide transcriptome analyses of the 'Knallgas' bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16 with regard to polyhydroxyalkanoate metabolism.Microbiology (Reading). 2010 Jul;156(Pt 7):2136-2152. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.038380-0. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Microbiology (Reading). 2010. PMID: 20395272
-
Improved polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production in transgenic tobacco by enhancing translation efficiency of bacterial PHB biosynthetic genes.J Biosci Bioeng. 2011 Apr;111(4):485-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.11.020. Epub 2010 Dec 24. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21185778
-
Absence of ppGpp Leads to Increased Mobilization of Intermediately Accumulated Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) in Ralstonia eutropha H16.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Jun 16;83(13):e00755-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00755-17. Print 2017 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28455332 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in the formation of polyhydroxyalkanoate granules (carbonosomes) and novel functions of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate).Environ Microbiol. 2014 Aug;16(8):2357-73. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12356. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24329995 Review.
Cited by
-
Microaerobic insights into production of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 3-hydroxyhexanoate via native reverse β-oxidation from glucose in Ralstonia eutropha H16.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Jan 14;23(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02294-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38221622 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium homeostasis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires multiple transporters and modulates swarming motility.Cell Calcium. 2013 Nov;54(5):350-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Cell Calcium. 2013. PMID: 24074964 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Toluene Degraders in the Rhizosphere of a Constructed Wetland Model Show Diurnal Polyhydroxyalkanoate Metabolism.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Jun 30;82(14):4126-4132. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00493-16. Print 2016 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27129963 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Characterization and Application of the PHA Synthase from Azotobacter vinelandii for the Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Containing 4-Hydroxybutyrate.Polymers (Basel). 2021 May 14;13(10):1576. doi: 10.3390/polym13101576. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069008 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of PHB Depolymerases in Ralstonia eutropha: Further Elucidation of the Roles of Enzymes in PHB Homeostasis.AMB Express. 2012 Apr 26;2(1):26. doi: 10.1186/2191-0855-2-26. AMB Express. 2012. PMID: 22537946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama, M., T. Tsuge, and Y. Doi. 2003. Environmental life cycle comparison of polyhydroxyalkanoates produced from renewable carbon resources by bacterial fermentation. Polym. Degradation Stab. 80:183-194.
-
- Chen, G.-Q., and Q. Wu. 2005. Microbial production and applications of chiral hydroxyalkanoates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 67:592-599. - PubMed
-
- Fisher, M., J. T. M. Kroon, W. Martindale, A. R. Stuitje, A. R. Slabas, and J. B. Rafferty. 2000. The X-ray structure of Brassica napus β-keto acyl carrier protein reductase and its implications for substrate binding and catalysis. Structure 8:339-347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

