Cytosolic phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipids in tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 20729478
- PMCID: PMC2943523
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djq290
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipids in tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer and glioblastoma multiforme are highly angiogenic and, despite advances in treatment, remain resistant to therapy. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA(2)) activation contributes to treatment resistance through transduction of prosurvival signals. We investigated cPLA(2) as a novel molecular target for antiangiogenesis therapy.
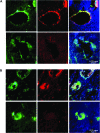
Methods: Glioblastoma (GL261) and Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) heterotopic tumor models were used to study the effects of cPLA(2) expression on tumor growth and vascularity in C57/BL6 mice wild type for (cPLA(2)α(+/+)) or deficient in (cPLA(2)α(-/-)) cPLA(2)α, the predominant isoform in endothelium (n = 6-7 mice per group). The effect of inhibiting cPLA(2) activity on GL261 and LLC tumor growth was studied in mice treated with the chemical cPLA(2) inhibitor 4-[2-[5-chloro-1-(diphenylmethyl)-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]-ethoxy]benzoic acid (CDIBA). Endothelial cell proliferation and function were evaluated by Ki-67 immunofluorescence and migration assays in primary cultures of murine pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (MPMEC) isolated from cPLA(2)α(+/+) and cPLA(2)α(-/-) mice. Proliferation, invasive migration, and tubule formation were assayed in mouse vascular endothelial 3B-11 cells treated with CDIBA. Effects of lysophosphatidylcholine, arachidonic acid, and lysophosphatidic acid (lipid mediators of tumorigenesis and angiogenesis) on proliferation and migration were examined in 3B-11 cells and cPLA(2)α(-/-) MPMEC. All statistical tests were two-sided.
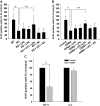
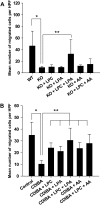
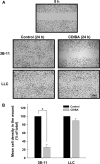
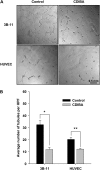
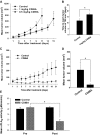
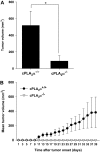
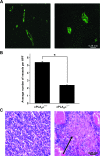
Results: GL261 tumor progression proceeded normally in cPLA(2)α(+/+) mice, whereas no GL261 tumors formed in cPLA(2)α(-/-) mice. In the LLC tumor model, spontaneous tumor regression was observed in 50% of cPLA(2)α(-/-) mice. Immunohistochemical examination of the remaining tumors from cPLA(2)α(-/-) mice revealed attenuated vascularity (P ≤ .001) compared with tumors from cPLA(2)α(+/+) mice. Inhibition of cPLA(2) activity by CDIBA resulted in a delay in tumor growth (eg, LLC model: average number of days to reach tumor volume of 700 mm(3), CDIBA vs vehicle: 16.8 vs 11.8, difference = 5, 95% confidence interval = 3.6 to 6.4, P = .04) and a decrease in tumor size (eg, GL261 model: mean volume on day 21, CDIBA vs vehicle: 40.1 vs 247.4 mm(3), difference = 207.3 mm(3), 95% confidence interval = 20.9 to 293.7 mm(3), P = .021). cPLA(2) deficiency statistically significantly reduced MPMEC proliferation and invasive migration (P = .002 and P = .004, respectively). Compared with untreated cells, cPLA(2)α(-/-) MPMEC treated with lysophosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidic acid displayed increased cell proliferation (P = .011) and invasive migration (P < .001).
Conclusions: In these mouse models of brain and lung cancer, cPLA(2) and lysophospholipids have key regulatory roles in tumor angiogenesis. cPLA(2) inhibition may be a novel effective antiangiogenic therapy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2{alpha} and cancer: a role in tumor angiogenesis.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Sep 22;102(18):1377-9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq324. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010. PMID: 20729476 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2{alpha} and cancer: a role in tumor angiogenesis.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Sep 22;102(18):1377-9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq324. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010. PMID: 20729476 No abstract available.
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2: targeting cancer through the tumor vasculature.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;15(5):1635-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1905. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19240173 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2-{alpha} as a novel mechanism regulating endothelial cell cycle progression and angiogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 27;284(9):5784-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807282200. Epub 2009 Jan 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19119141 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and function of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha at the Golgi.Biochimie. 2010 Jun;92(6):620-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.03.001. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20226226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical properties and pathophysiological roles of cytosolic phospholipase A2s.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Nov;1761(11):1317-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.08.001. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16962823 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards novel radiosensitizing agents: the role of cytosolic PLA2α in combined modality cancer therapy.Future Med Chem. 2011 May;3(7):835-43. doi: 10.4155/fmc.11.38. Future Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21644828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channel Expression Signatures in Tumor-Derived Endothelial Cells: Functional Roles in Prostate Cancer Angiogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 8;11(7):956. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070956. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31288452 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular oxidative stress response mediates radiosensitivity in Fus1-deficient mice.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Feb 19;6(2):e1652. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.593. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25695605 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α Induces Apoptosis in Multiple Myeloma Cells.Molecules. 2021 Dec 9;26(24):7447. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247447. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946532 Free PMC article.
-
A VE-cadherin-PAR3-α-catenin complex regulates the Golgi localization and activity of cytosolic phospholipase A(2)α in endothelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(9):1783-96. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0694. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22398721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clamon G, Herndon J, Cooper R, Chang AY, Rosenman J, Green MR. Radiosensitization with carboplatin for patients with unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(1):4–11. - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis LM. Brain tumors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(2):114–123. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Machtay M, Kaiser LR, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic factors in patients treated with surgery and postoperative radiation therapy. Radiology. 1999;213(3):845–852. - PubMed
-
- Wagner H., Jr Postoperative adjuvant therapy for patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer: still controversial after all these years. Chest. 2000;117(4) suppl 1:110S–118S. - PubMed
-
- Riely GJ, Miller VA. Vascular endothelial growth factor trap in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(15, pt 2):s4623–s4627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

