fMRI BOLD response in high-risk college students (Part 1): during exposure to alcohol, marijuana, polydrug and emotional picture cues
- PMID: 20729530
- PMCID: PMC2930251
- DOI: 10.1093/alcalc/agq042
fMRI BOLD response in high-risk college students (Part 1): during exposure to alcohol, marijuana, polydrug and emotional picture cues
Abstract
Aim: This functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study examined reactivity to alcohol, polydrug, marijuana and emotional picture cues in students who were referred to a college alcohol and drug assistance program.
Methods: The fMRI data of 10 participants (5 females; 5 males) were collected while they viewed standardized emotional and appetitive cues.
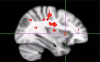
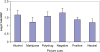
Results: Positive and negative emotional cues produced greater activity than neutral cues in the expected brain areas. Compared with neutral cues, alcohol cues produced greater brain activation in the right insula, left anterior cingulate, left caudate and left prefrontal cortex (Z = 2.01, 1.86, 1.82, 1.81, respectively; P < 0.05). Drug cues produced significantly greater left prefrontal activity compared with neutral cues, with polydrug cues activating the right insula and marijuana cues activating left anterior cingulate.
Conclusions: Students at-risk for alcohol abuse showed neural reactivity to alcohol cues in four brain regions, which is consistent with their greater use of alcohol. Insula activation to appetitive cues may be an early marker of risk for progression to alcohol/drug abuse.
Figures


Similar articles
-
fMRI BOLD response of high-risk college students (Part 2): during memory priming of alcohol, marijuana and polydrug picture cues.Alcohol Alcohol. 2010 Sep-Oct;45(5):444-8. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agq043. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Alcohol Alcohol. 2010. PMID: 20729527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) response to alcohol pictures predicts subsequent transition to heavy drinking in college students.Addiction. 2014 Apr;109(4):585-95. doi: 10.1111/add.12437. Epub 2014 Jan 19. Addiction. 2014. PMID: 24304235 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of alcohol use and family history of alcoholism on neural response to alcohol cues in college drinkers.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Jan;37 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):E161-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01879.x. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 23078363 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between fMRI response during a nonverbal memory task and marijuana use in college students.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Jul 1;188:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018. PMID: 29754029 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neurobiological correlates of cue-reactivity in alcohol-use disorders: A voxel-wise meta-analysis of fMRI studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Sep;128:294-310. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.031. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34171325 Review.
Cited by
-
The neural correlates of the unified percept of alcohol-related craving: a fMRI and EEG study.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18471-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343732 Free PMC article.
-
Medial parietal cortex activation related to attention control involving alcohol cues.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Dec 20;4:174. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00174. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24391604 Free PMC article.
-
BNST-insula structural connectivity in humans.Neuroimage. 2020 Apr 15;210:116555. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116555. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31954845 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of sensitivity to alcohol by cortical and thalamic brain regions.Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Oct;44(8):2569-2580. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13374. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Eur J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27543844 Free PMC article.
-
High and low sensation seeking adolescents show distinct patterns of brain activity during reward processing.Neuroimage. 2013 Feb 1;66:184-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.003. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23142276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaro E, Barker GJ. Study design in fMRI: basic principle. Brain Cognition. 2006;60:220–232. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2005.11.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnosis and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Barnett NP, Read JP. Mandatory alcohol intervention for alcohol-abusing college students: a systematic view. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2005;29:147–58. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2005.05.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breiter HC, Gollub RL, Weisskoff RM, et al. Acute effects of cocaine on human brain activity and emotion. Neuron. 1997;19:591–611. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80374-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brody AL, Mandelkern MA, London ED, et al. Brain metabolic changes during cigarette craving. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:1162–1172. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.59.12.1162. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

