Lipid binding requirements for oxysterol-binding protein Kes1 inhibition of autophagy and endosome-trans-Golgi trafficking pathways
- PMID: 20729555
- PMCID: PMC2962487
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.147264
Lipid binding requirements for oxysterol-binding protein Kes1 inhibition of autophagy and endosome-trans-Golgi trafficking pathways
Abstract
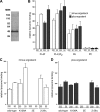
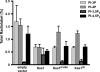
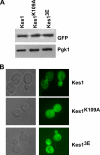
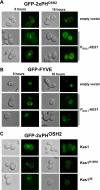
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein Kes1/Osh4 is a member of the enigmatic family of oxysterol-binding proteins found throughout Eukarya united by a β-barrel structure that binds sterols and oxysterols. In this study, we determined that phosphoinositides are the major determinant in membranes that facilitate Kes1 association both in vitro and in cells. Increased expression of Kes1 in yeast cells decreased the levels of both phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P). Phosphoinositide and sterol bindings by Kes1 were necessary for Kes1 to decrease the level of PI4P but not PI3P. Kes1 inhibited vesicular trafficking between the trans-Golgi and plasma membrane as evidenced by accumulation of the vacuolar soluble NSF attachment protein receptors Snc1 in the cytoplasmic vesicles. Sterol and phosphoinositide binding by Kes1 both contributed to its regulation of Snc1 trafficking. This study also describes a previously unknown role for Kes1 in the regulation of the autophagy/cytoplasm to the vacuole trafficking pathway. The Kes1-mediated regulation of the autophagy/cytoplasm to the vacuole trafficking pathway was prevented by increasing expression of the PI3K Vps34, suggesting that it is the Kes1-mediated decrease in PI3P level that contributes to this regulation.
Figures
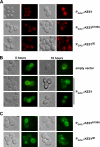
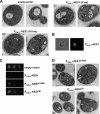


Similar articles
-
The yeast oxysterol binding protein Kes1 maintains sphingolipid levels.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 4;8(4):e60485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060485. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593226 Free PMC article.
-
A Lipid Transfer Protein Signaling Axis Exerts Dual Control of Cell-Cycle and Membrane Trafficking Systems.Dev Cell. 2018 Feb 5;44(3):378-391.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.12.026. Epub 2018 Jan 27. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 29396115 Free PMC article.
-
A budding yeast-centric view of oxysterol binding protein family function.Adv Biol Regul. 2025 Jan;95:101061. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2024.101061. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Adv Biol Regul. 2025. PMID: 39613716 Review.
-
The sterol-binding protein Kes1/Osh4p is a regulator of polarized exocytosis.Traffic. 2011 Nov;12(11):1521-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01265.x. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21819498
-
Surprising roles for phospholipid binding proteins revealed by high throughput genetics.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;88(4):565-74. doi: 10.1139/O09-171. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20651827 Review.
Cited by
-
NuA4 Lysine Acetyltransferase Complex Contributes to Phospholipid Homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jun 7;7(6):1799-1809. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.041053. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28455416 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast oxysterol binding protein Kes1 maintains sphingolipid levels.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 4;8(4):e60485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060485. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593226 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the role of sterol metabolism in antifungal drug resistance: a mini-review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1409085. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1409085. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39464401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localization of lipid raft proteins to the plasma membrane is a major function of the phospholipid transfer protein Sec14.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055388. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383173 Free PMC article.
-
The Endoplasmic Reticulum-Plasma Membrane Tethering Protein Ice2 Controls Lipid Droplet Size via the Regulation of Phosphatidylcholine in Candida albicans.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;10(1):87. doi: 10.3390/jof10010087. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beh C. T., Rine J. (2004) J. Cell Sci. 117, 2983–2996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

