Ku prevents Exo1 and Sgs1-dependent resection of DNA ends in the absence of a functional MRX complex or Sae2
- PMID: 20729809
- PMCID: PMC2957202
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.193
Ku prevents Exo1 and Sgs1-dependent resection of DNA ends in the absence of a functional MRX complex or Sae2
Abstract
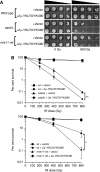
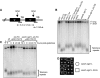
In this study, we investigate the interplay between Ku, a central non-homologous end-joining component, and the Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 (MRX) complex and Sae2, end-processing factors crucial for initiating 5'-3' resection of double-strand break (DSB) ends. We show that in the absence of end protection by Ku, the requirement for the MRX complex is bypassed and resection is executed by Exo1. In contrast, both the Exo1 and Sgs1 resection pathways contribute to DSB processing in the absence of Ku and Sae2 or when the MRX complex is intact, but functionally compromised by elimination of the Mre11 nuclease activity. The ionizing radiation sensitivity of a mutant defective for extensive resection (exo1Δ sgs1Δ) cannot be suppressed by the yku70Δ mutation, indicating that Ku suppression is specific to the initiation of resection. We provide evidence that replication-associated DSBs need to be processed by Sae2 for repair by homologous recombination unless Ku is absent. Finally, we show that the presence of Ku exacerbates DNA end-processing defects established in the sae2Δ sgs1Δ mutant, leading to its lethality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Adamo A, Collis SJ, Adelman CA, Silva N, Horejsi Z, Ward JD, Martinez-Perez E, Boulton SJ, La Volpe A (2010) Preventing nonhomologous end joining suppresses DNA repair defects of Fanconi anemia. Mol Cell 39: 25–35 - PubMed
-
- Bae SH, Bae KH, Kim JA, Seo YS (2001) RPA governs endonuclease switching during processing of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes. Nature 412: 456–461 - PubMed
-
- Bonetti D, Martina M, Clerici M, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2009) Multiple pathways regulate 3′ overhang generation at S cerevisiae telomeres. Mol Cell 35: 70–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

