Analysis of microtubule dynamic instability using a plus-end growth marker
- PMID: 20729842
- PMCID: PMC3032800
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1493
Analysis of microtubule dynamic instability using a plus-end growth marker
Abstract
Regulation of microtubule dynamics is essential for many cell biological processes and is likely to be variable between different subcellular regions. We describe a computational approach to analyze microtubule dynamics by detecting growing microtubule plus ends. Our algorithm tracked all EB1-EGFP comets visible in an image time-lapse sequence allowing the detection of spatial patterns of microtubule dynamics. We introduce spatiotemporal clustering of EB1-EGFP growth tracks to infer microtubule behaviors during phases of pause and shortening. We validated the algorithm by comparing the results to data for manually tracked, homogeneously labeled microtubules and by analyzing the effects of well-characterized inhibitors of microtubule polymerization dynamics. We used our method to analyze spatial variations of intracellular microtubule dynamics in migrating epithelial cells.
Figures
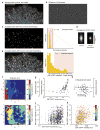
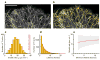
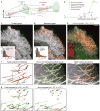
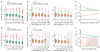
Comment in
-
Acquisition frame rate affects microtubule plus-end tracking analysis.Nat Methods. 2014 Mar;11(3):219-20. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2846. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 24577268 No abstract available.
-
Reply to "Acquisition frame rate affects microtubule plus-end tracking analysis".Nat Methods. 2014 Mar;11(3):220. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2860. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 24577269 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

