14-3-3 adaptor proteins recruit AID to 5'-AGCT-3'-rich switch regions for class switch recombination
- PMID: 20729863
- PMCID: PMC3645988
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1884
14-3-3 adaptor proteins recruit AID to 5'-AGCT-3'-rich switch regions for class switch recombination
Abstract
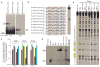
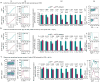
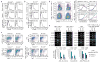
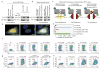
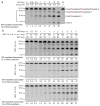
Class switch DNA recombination (CSR) is the mechanism that diversifies the biological effector functions of antibodies. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a key protein in CSR, targets immunoglobulin H (IgH) switch regions, which contain 5'-AGCT-3' repeats in their core. How AID is recruited to switch regions remains unclear. Here we show that 14-3-3 adaptor proteins have an important role in CSR. 14-3-3 proteins specifically bound 5'-AGCT-3' repeats, were upregulated in B cells undergoing CSR and were recruited with AID to the switch regions that are involved in CSR events (Smu-->Sgamma1, Smu-->Sgamma3 or Smu-->Salpha). Moreover, blocking 14-3-3 by difopein, 14-3-3gamma deficiency or expression of a dominant-negative 14-3-3sigma mutant impaired recruitment of AID to switch regions and decreased CSR. Finally, 14-3-3 proteins interacted directly with AID and enhanced AID-mediated in vitro DNA deamination, further emphasizing the important role of these adaptors in CSR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

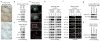


References
-
- Maizels N. Immunoglobulin gene diversification. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:23–46. - PubMed
-
- Casali P. Somatic recombination and hypermutation in the immune system. In: Krebs JE, Goldstein ES, Kilpatrick ST, editors. Lewin's Genes X. Jones & Bartlett; Sudbury, MA: 2011. pp. 570–623.
-
- Odegard VH, Schatz DG. Targeting of somatic hypermutation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:573–583. - PubMed
-
- Teng G, Papavasiliou FN. Immunoglobulin somatic hypermutation. Annu Rev Genet. 2007;41:107–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 GM103533/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040908/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI045011/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA116676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI 079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 045011/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 060573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR011823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA 116676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045011/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

