CD4+ CD25+ but not CD4+ Foxp3+ T cells as a regulatory subset in primary biliary cirrhosis
- PMID: 20729906
- PMCID: PMC4002956
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2010.40
CD4+ CD25+ but not CD4+ Foxp3+ T cells as a regulatory subset in primary biliary cirrhosis
Abstract
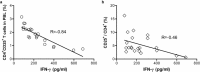
Increasing evidence indicates a role for regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the immune response and in autoimmune diseases, but the role of Tregs and cytokines in autoimmune hepatic diseases remains largely unclear and controversial, especially in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). This study was undertaken to investigate Tregs and different cytokines in the liver and peripheral blood of PBC patients. We found that these patients demonstrated a reduction of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells but elevated CD4(+)Foxp3(+) T cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and CD4(+) T cells. The percentage of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in PBMCs was negatively correlated with elevated plasma interferon (IFN)-γ levels. A liver-specific analysis showed that the frequency of Foxp3(+) Tregs, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and IFN-γ were increased in PBC patients. Our findings suggest that an imbalance between CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs and cytotoxic cytokines plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of PBC while the role of Foxp3 needs further investigation.
Figures


References
-
- Kaplan MM, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Prince M, Chetwynd A, Newman WL, Metcalf JV, James OF. Survival and symptom progression in a geographically based cohort of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: follow-up for up to 28 years. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1044–1051. - PubMed
-
- Jones DE. Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2003;39:639–648. - PubMed
-
- Jones DE. Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Denning TL, Wang YC, Patel SR, Williams IR, Pulendran B. Lamina propria macrophages and dendritic cells differentially induce regulatory and interleukin 17-producing T cell responses. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1086–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

