ALDH1L1 inhibits cell motility via dephosphorylation of cofilin by PP1 and PP2A
- PMID: 20729910
- PMCID: PMC2992098
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.356
ALDH1L1 inhibits cell motility via dephosphorylation of cofilin by PP1 and PP2A
Abstract
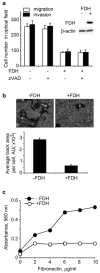
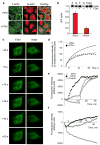
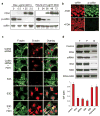
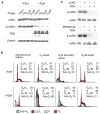
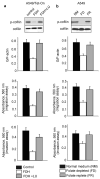
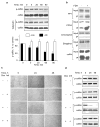
Here we report that ALDH1L1 (FDH, a folate enzyme with tumor suppressor-like properties) inhibits cell motility. The underlying mechanism involves F-actin stabilization, re-distribution of cytoplasmic actin toward strong preponderance of filamentous actin and formation of actin stress fibers. A549 cells expressing FDH showed a much slower recovery of green fluorescent protein-actin fluorescence in a fluorescence recovery after photobleaching assay, as well as an increase in G-actin polymerization and a decrease in F-actin depolymerization rates in pyren-actin fluorescence assays indicating the inhibition of actin dynamics. These effects were associated with robust dephosphorylation of the actin depolymerizing factor cofilin by PP1 and PP2A serine/threonine protein phosphatases, but not the cofilin-specific phosphatases slingshot and chronophin. In fact, the PP1/PP2A inhibitor calyculin prevented cofilin dephosphorylation and restored motility. Inhibition of FDH-induced apoptosis by the Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125 or the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk did not restore motility or levels of phosphor-cofilin, indicating that the observed effects are independent of FDH function in apoptosis. Interestingly, cofilin small interfering RNA or expression of phosphorylation-deficient S3A cofilin mutant resulted in a decrease of G-actin and the actin stress fiber formation, the effects seen upon FDH expression. In contrast, the expression of S3D mutant, mimicking constitutive phosphorylation, prevented these effects further supporting the cofilin-dependent mechanism. Dephosphorylation of cofilin and inhibition of motility in response to FDH can also be prevented by the increased folate in media. Furthermore, folate depletion itself, in the absence of FDH, resulted in cofilin dephosphorylation and inhibition of motility in several cell lines. Our experiments showed that these effects were folate specific and not a general response to nutrient starvation. Overall, this study shows the presence of distinct intracellular signaling pathways regulating motility in response to folate status and points toward mechanisms involving folates in promoting a malignant phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D1 regulates cofilin-mediated F-actin reorganization and cell motility through slingshot.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 May;11(5):545-56. doi: 10.1038/ncb1861. Epub 2009 Mar 29. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19329994 Free PMC article.
-
Actin-depolymerizing factor and cofilin-1 play overlapping roles in promoting rapid F-actin depolymerization in mammalian nonmuscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):649-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0555. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15548599 Free PMC article.
-
A receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1)-independent necrotic death under the control of protein phosphatase PP2A that involves the reorganization of actin cytoskeleton and the action of cofilin-1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25699-710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575134. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25096578 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of ALDH1L1 folate enzyme confers a selective metabolic advantage for tumor progression.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Apr 1;302:149-155. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.02.013. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30794800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cofilin phosphatases and regulation of actin dynamics.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;18(1):26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16337782 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial translocation and interaction of cofilin and Drp1 are required for erucin-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 30;6(3):1834-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2795. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25595902 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals novel phosphorylation events in insulin signaling regulated by protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12A.J Proteomics. 2014 Sep 23;109:63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24972320 Free PMC article.
-
The Binding Receptors of Aβ: an Alternative Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):455-471. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8994-0. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25465238 Review.
-
Folate-conjugated immunoglobulin targets melanoma tumor cells for NK cell effector functions.Melanoma Res. 2016 Aug;26(4):329-37. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000258. Melanoma Res. 2016. PMID: 27035691 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming by Folate Restriction Leads to a Less Aggressive Cancer Phenotype.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Feb;15(2):189-200. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0317. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28108628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambach A, Saunus J, Konstandin M, Wesselborg S, Meuer SC, Samstag Y. The serine phosphatases PP1 and PP2A associate with and activate the actin-binding protein cofilin in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:3422–31. - PubMed
-
- Ballestrem C, Wehrle-Haller B, Imhof BA. Actin dynamics in living mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 1998;111(Pt 12):1649–58. - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR, Wiggan OP. ADF/cofilin and actin dynamics in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:598–605. - PubMed
-
- Chanson A, Sayd T, Rock E, Chambon C, Sante-Lhoutellier V, Potier de Courcy G, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals changes in the liver protein pattern of rats exposed to dietary folate deficiency. J Nutr. 2005;135:2524–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

