Surface Plasmon-Coupled Emission with Gold Films
- PMID: 20729993
- PMCID: PMC2924592
- DOI: 10.1021/jp040221h
Surface Plasmon-Coupled Emission with Gold Films
Abstract
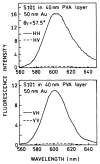
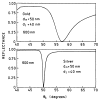
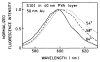
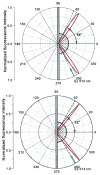
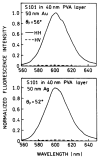
In a recent report we demonstrated efficient collection of emission by coupling to surface plasmons on a thin silver film, resulting in a directional signal in the glass substrate. We call the phenomenon surface plasmon coupled emission (SPCE). In the present report we examined sulforhodamine 101 (S101) in thin polymer films on 50 nm thick gold films on glass. We observed efficient SPCE through thin gold films. This result was surprising because metallic gold is typically an efficient quencher of fluorescence. The energy effectively coupled through the gold film into the glass at a sharply defined angle, but somewhat less sharp than for a comparable silver film. About 50% of the total emission appeared as SPCE, irrespective of direct excitation or excitation via the plasmon resonance evanescent wave. The emission was p-polarized with different wavelengths appearing at different angles. The lifetime of S101 was mostly unaffected by the gold film. These results indicate that SPCE occurs over long distances, larger than for quenching by energy transfer to the gold. We conclude highly efficient detection devices can be constructed by using fluorophores on gold-coated surfaces.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
