Astrocytic gap junctional communication is reduced in amyloid-β-treated cultured astrocytes, but not in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
- PMID: 20730033
- PMCID: PMC2922840
- DOI: 10.1042/AN20100017
Astrocytic gap junctional communication is reduced in amyloid-β-treated cultured astrocytes, but not in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice
Abstract
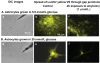
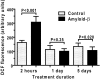
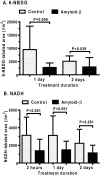
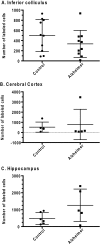
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by accumulation of amyloid deposits in brain, progressive cognitive deficits and reduced glucose utilization. Many consequences of the disease are attributed to neuronal dysfunction, but roles of astrocytes in its pathogenesis are not well understood. Astrocytes are extensively coupled via gap junctions, and abnormal trafficking of metabolites and signalling molecules within astrocytic syncytia could alter functional interactions among cells comprising the neurovascular unit. To evaluate the influence of amyloid-beta on astrocyte gap junctional communication, cultured astrocytes were treated with monomerized amyloid-β(1-40) (1 μmol/l) for intervals ranging from 2 h to 5 days, and the areas labelled by test compounds were determined by impaling a single astrocyte with a micropipette and diffusion of material into coupled cells. Amyloid-β-treated astrocytes had rapid, sustained 50-70% reductions in the area labelled by Lucifer Yellow, anionic Alexa Fluor® dyes and energy-related compounds, 6-NBDG (a fluorescent glucose analogue), NADH and NADPH. Amyloid-β treatment also caused a transient increase in oxidative stress. In striking contrast with these results, spreading of Lucifer Yellow within astrocytic networks in brain slices from three regions of 8.5-14-month-old control and transgenic Alzheimer's model mice was variable, labelling 10-2000 cells; there were no statistically significant differences in the number of dye-labelled cells among the groups or with age. Thus amyloid-induced dysfunction of gap junctional communication in cultured astrocytes does not reflect the maintenance of dye transfer through astrocytic syncytial networks in transgenic mice; the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease is not appropriately represented by the cell culture system.
Keywords: 6-NBDG, 6-[N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)amino]-6-deoxyglucose; A350, Alexa Fluor® 350; A568, Alexa Fluor® 568; APP, amyloid-β precursor protein; Cx, connexin; DCF, dichlorofluorescein; DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; FBS, fetal bovine serum; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; H2DCF-DA, carboxydihydrodichlorofluorescein diacetate; L-LME, L-leucine methyl ester hydrochloride; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SR101, sulforhodamine 101; STZ, streptozotocin; aCSF, artificial cerebral spinal fluid; amyloid protein; astrocyte; connexin; dBcAMP, dibutyryl cAMP; dye transfer; gap junction; metabolite trafficking.
Figures






References
-
- Abe T, Takahashi S, Suzuki N. Oxidative metabolism in cultured rat astroglia: effects of reducing the glucose concentration in the culture medium and of d-aspartate or potassium stimulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Abramov AY, Canevari L, Duchen MR. Calcium signals induced by amyloid β peptide and their consequences in neurons and astrocytes in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1742:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Chen K, Pietrini P, Rapoport SI, Reiman EM. Longitudinal PET evaluation of cerebral metabolic decline in dementia: a potential outcome measure in Alzheimer's disease treatment studies. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:738–745. - PubMed
-
- Aller CB, Ehmann S, Gilman-Sachs A, Snyder AK. Flow cytometric analysis of glucose transport by rat brain cells. Cytometry. 1997;27:262–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

