The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 improves recovery of human embryonic stem cells after fluorescence-activated cell sorting with multiple cell surface markers
- PMID: 20730054
- PMCID: PMC2921395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012148
The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 improves recovery of human embryonic stem cells after fluorescence-activated cell sorting with multiple cell surface markers
Abstract
Background: Due to the inherent sensitivity of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) to manipulations, the recovery and survival of hESCs after fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) can be low. Additionally, a well characterized and robust methodology for performing FACS on hESCs using multiple-cell surface markers has not been described. The p160-Rho-associated coiled kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, Y-27632, previously has been identified as enhancing survival of hESCs upon single-cell dissociation, as well as enhancing recovery from cryopreservation. Here we examined the application of Y-27632 to hESCs after FACS to improve survival in both feeder-dependent and feeder-independent growth conditions.
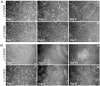
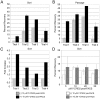
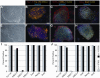
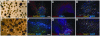
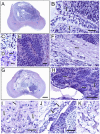
Methodology/principal findings: HESCs were sorted using markers for SSEA-3, TRA-1-81, and SSEA-1. Cells were plated after sorting for 24 hours in either the presence or the absence of Y-27632. In both feeder-dependent and feeder-independent conditions, cell survival was greater when Y-27632 was applied to the hESCs after sort. Specifically, treatment of cells with Y-27632 improved post-sort recovery up to four fold. To determine the long-term effects of sorting with and without the application of Y-27632, hESCs were further analyzed. Specifically, hESCs sorted with and without the addition of Y-27632 retained normal morphology, expressed hESC-specific markers as measured by immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry, and maintained a stable karyotype. In addition, the hESCs could differentiate into three germ layers in vitro and in vivo in both feeder-dependent and feeder-independent growth conditions.
Conclusions/significance: The application of Y-27632 to hESCs after cell sorting improves cell recovery with no observed effect on pluripotency, and enables the consistent recovery of hESCs by FACS using multiple surface markers. This improved methodology for cell sorting of hESCs will aid many applications such as removal of hESCs from secondary cell types, identification and isolation of stem cell subpopulations, and generation of single cell clones. Finally, these results demonstrate an additional application of ROCK inhibition to hESC research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 on normal and variant human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) in vitro: its benefits in hESC expansion.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010 Mar;6(1):86-95. doi: 10.1007/s12015-009-9107-8. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010. PMID: 20013076
-
Presence of a ROCK inhibitor in extracellular matrix supports more undifferentiated growth of feeder-free human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells upon passaging.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010 Mar;6(1):96-107. doi: 10.1007/s12015-009-9103-z. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010. PMID: 20012714
-
Enhanced generation of human embryonic stem cells from single blastomeres of fair and poor-quality cleavage embryos via inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase β and Rho-associated kinase signaling.Hum Reprod. 2013 Oct;28(10):2661-71. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det309. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23925393
-
Application of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor to human pluripotent stem cells.J Biosci Bioeng. 2012 Dec;114(6):577-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.07.013. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012. PMID: 22898436 Review.
-
Stimulating progress in regenerative medicine: improving the cloning and recovery of cryopreserved human pluripotent stem cells with ROCK inhibitors.Regen Med. 2010 Sep;5(5):799-807. doi: 10.2217/rme.10.45. Regen Med. 2010. PMID: 20868334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin accessibility dynamics of neurogenic niche cells reveal defects in neural stem cell adhesion and migration during aging.Nat Aging. 2023 Jul;3(7):866-893. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00449-3. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37443352 Free PMC article.
-
A novel platform to enable the high-throughput derivation and characterization of feeder-free human iPSCs.Sci Rep. 2012;2:213. doi: 10.1038/srep00213. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22355727 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Engraftment of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes via a Transient Inhibition of Rho Kinase Activity.J Vis Exp. 2019 Jul 10;(149):10.3791/59452. doi: 10.3791/59452. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31355804 Free PMC article.
-
Non-colony type monolayer culture of human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res. 2012 Nov;9(3):237-48. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Stem Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22910561 Free PMC article.
-
Culture and differentiation of rabbit intestinal organoids and organoid-derived cell monolayers.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 8;11(1):5401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84774-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33686141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A, Bongso A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman LM, Carpenter MK. Characterization and culture of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:699–708. - PubMed
-
- Trounson A. The production and directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:208–219. - PubMed
-
- Narumiya S, Ishizaki T, Uehata M. Use and properties of ROCK-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Methods Enzymol. 2000;325:273–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

